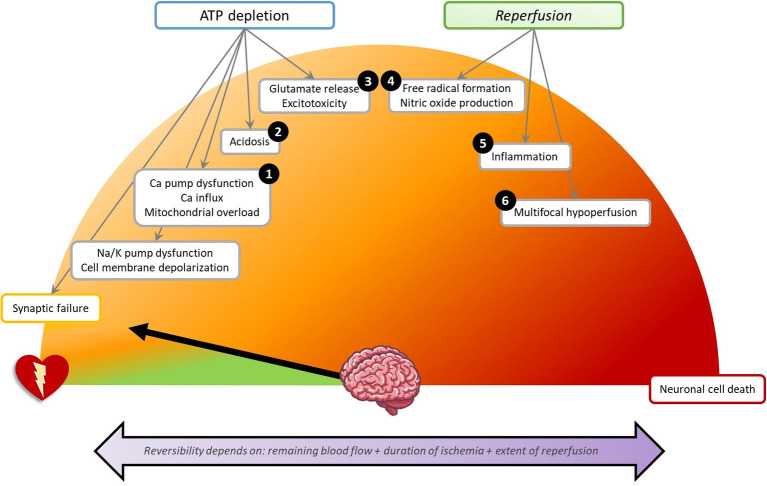
Figure 3.
Schematic overview of pathophysiology of brain damage in the first 72 h after cardiac arrest. Each step can lead to direct or delayed neuronal cell death. The numbers indicate the presumed point of action of the discussed neuroprotective treatments. (1) Calcium antagonists: Nimodipine, Flunarizine, Lidoflazine. Mitigating mitochondrial damage: Cyclosporine, Coenzyme Q10. (2) Preventing acidosis: Sodium bicarbonate. (3) Glutamate antagonism: Noble gases, Exenatide, Scopolamine, and penehyclidine hydrochloride, Magnesium. (4) Antioxidants: Preventing hyperoxia, Sodium nitrite. (5) Anti-inflammation: Erythropoietin, Glucocorticoids. (6) Optimizing cerebral perfusion: Adrenaline, Mild hypocapnia, High mean arterial pressure, Thrombolysis. (1–6) Pan-inhibition: Hypothermia. Not indicated by a number: Decreasing cerebral metabolism: Barbiturates. Supportive therapies: Sedation, Glucose regulation, Prophylactic antibiotics. Na/K, sodium/potassium; Ca, calcium.