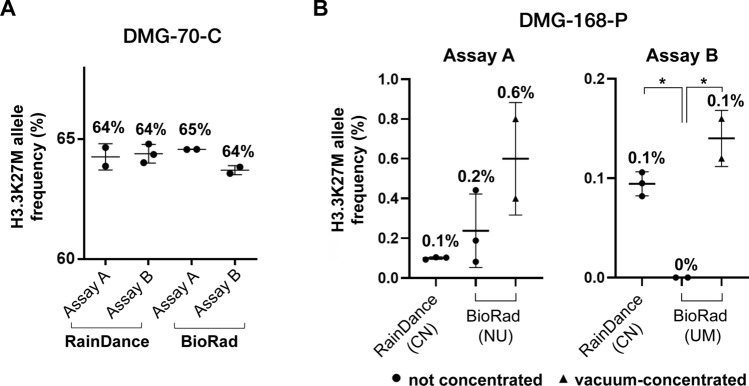
Figure 2.
Optimization of ctDNA detection across technical platforms and institutions. ctDNA extracted from CSF (DMG-70-C) and plasma (DMG-168-P) samples were analyzed for H3K27M mutation on BioRad and RainDance platforms at multiple institutions (CN, NU, UM). (A) CSF-derived ctDNA ddPCR results. CSF-derived ctDNA was pre-amplified at CN prior to ddPCR analysis. A 12 µL of sample was analyzed on the RainDance platform (CN), and 1 µL analyzed on the BioRad platform (UM). Fewer positive droplets were detected on the BioRad compared to the RainDance platform, while MAF remained similar across platforms and institutions. (B) Plasma-derived ctDNA analysis. Plasma-derived ctDNA was pre-amplified at CN via conventional PCR, using Assay A (right) and Assay B (left) primer/probe sets, prior to ddPCR analysis with Assay A across institutions. Speed vacuum concentration of samples was necessary to ensure preservation of input DNA in the requisite smaller sample input volume for the BioRad instrument. Superior test sensitivity was observed on the RainDance platform with both assays, while vacuum concentration increased observed MAF after Assay B ddPCR on the BioRad platform (t-test). % values = Mutation Allelic Frequency (MAF); * = Statistically significant difference in MAF (t-test, p < 0.05).