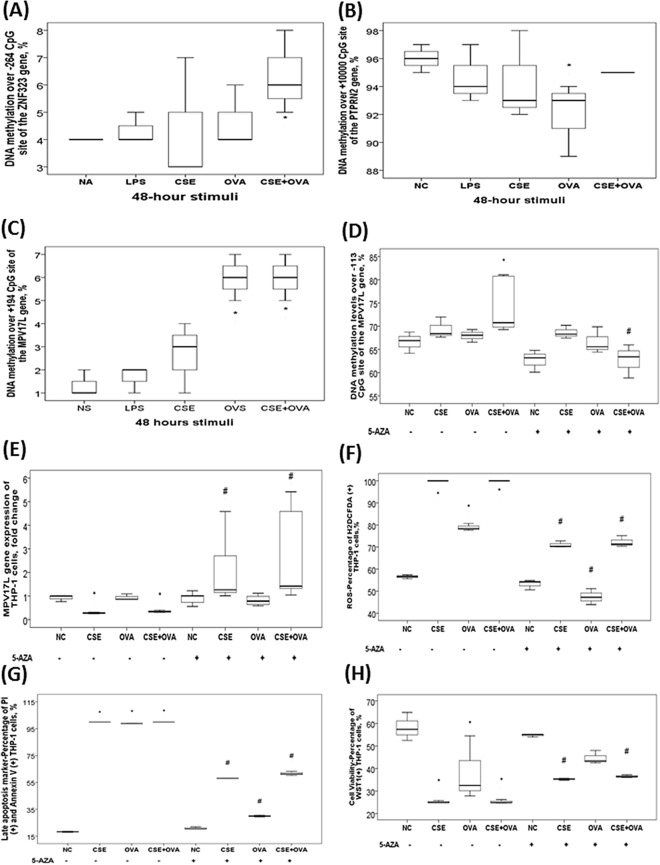
Figure 4.
Aberrant DNA methylation and corresponding gene expression changes of the candidate genes in THP-1 cells in response to in vitro cigarette smoke extract (CSE) plus ovalbumin (OVA) allergen stimuli. (A) DNA methylation level of the ZNF323 gene (-264) was increased in response to CSE plus OVA treatment. (B) DNA methylation level of the PTPRN2 gene (+ 10,000) was decreased with OVA stimuli. (C) DNA methylation levels over + 194 CpG site of the MPV17L gene were increased in response to OVA alone or CSE plus OVA concurrent treatment. Pre-treatment with de-methylation agent (5-AZA) resulted in (D) decreased DNA methylation levels over -113 CpG site of the MPV17L gene, (E) increased MPV17L gene expression, (F) reduced reactive oxygen species (ROS) production (percentage of H2DCFDA positive cells), (G) reduced late apoptosis (percentage of Annexin V and PI double positive cells), and (H) increased cell viability (percentage of WST-1 positive cells), as compared with that of CSE, OVA, or CSE plus OVA treatment alone. *p < 0.05 compared between normal control (NC; culture medium) and specific stimuli by Kruskal Wallis H-test. #p < 0.05 compared between the comparative groups with and without 5-AZA supplement by Kruskal Wallis H-test.