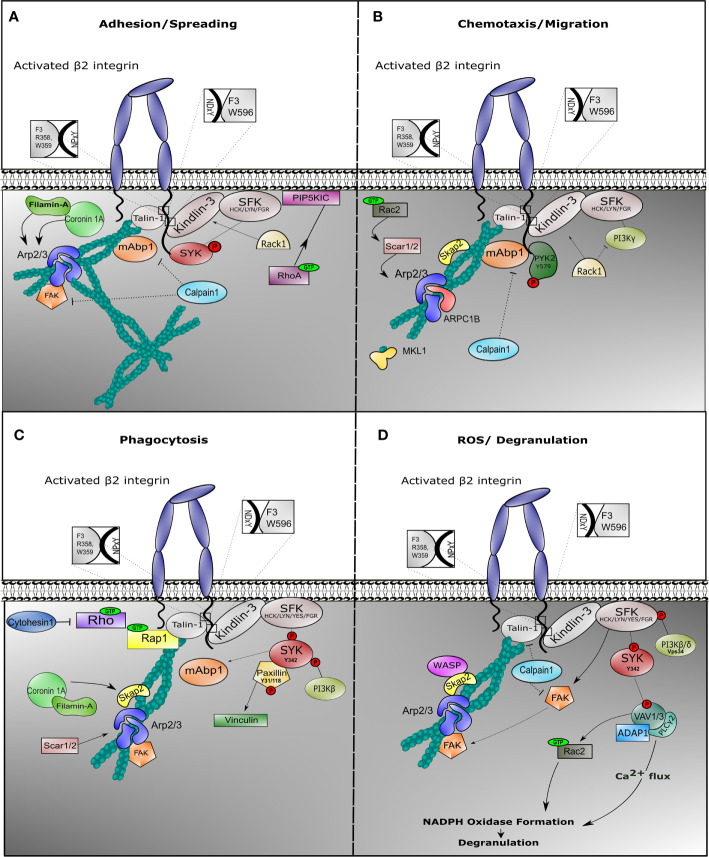
Figure 2.
Outside-in signaling involves different protein complexes in response to neutrophil effector function. Once β2 integrin is activated on neutrophils, outside-in signaling is facilitated in order to induce cell effector function. Neutrophils are endowed with multiple mechanism, all achieving target elimination. In all cases, integrin outside-in signaling involves stable interaction with Talin-1 and Kindlin-3, which recruits binding of the actin cytoskeleton and induction of signaling via Sarcoma family kinases (SFKs). During spreading (A), SFKs phosphorylate and recruit SYK to the cytoplasmic tail of the β2 integrin, while Phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate 5-kinase (PIP5KIC) induces activation of RhoA GTPase. Mitogen-activated binding protein 1 (mAbp1) is involved in stabilization of actin cytoskeleton, while Calpain-1 could play a role to negatively regulate its function. During migration (B), phosphorylated PYK2 is recruited and the Arp2/3 complex is stabilized via SKAP2 and Rac2 GTPase. Filamin A and ARPC1B are important for migration. We do not show WASP protein because deficiency results in impaired neutrophil migration in murine models only. Particularly during phagocytosis (C), phosphorylation of tyrosine protein kinase SYK induces binding of phosphorylated Paxillin with subsequent activation of Vinculin and activation of Phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3Kβ) and mAbp1. SCAR1/2 protein (also known as WAVE1/2) recruits Arp2/3 complex to stabilize actin cytoskeleton, while SKAP2 (or SKAP55R) functions as adaptor protein. During ROS production (D), degranulation is facilitated through increase of calcium influx. Phosphorylation of SYK initiates VAV phosphorylation with ADAP1 and PLCγ2 complex formation, promoting oxidative burst. VAV induces Rac1 GTPase activity, which facilitates NAPDH oxidase formation. In this context, Calpain1 could additionally inhibit Talin-1 or Focal adhesion kinase (FAK) function.