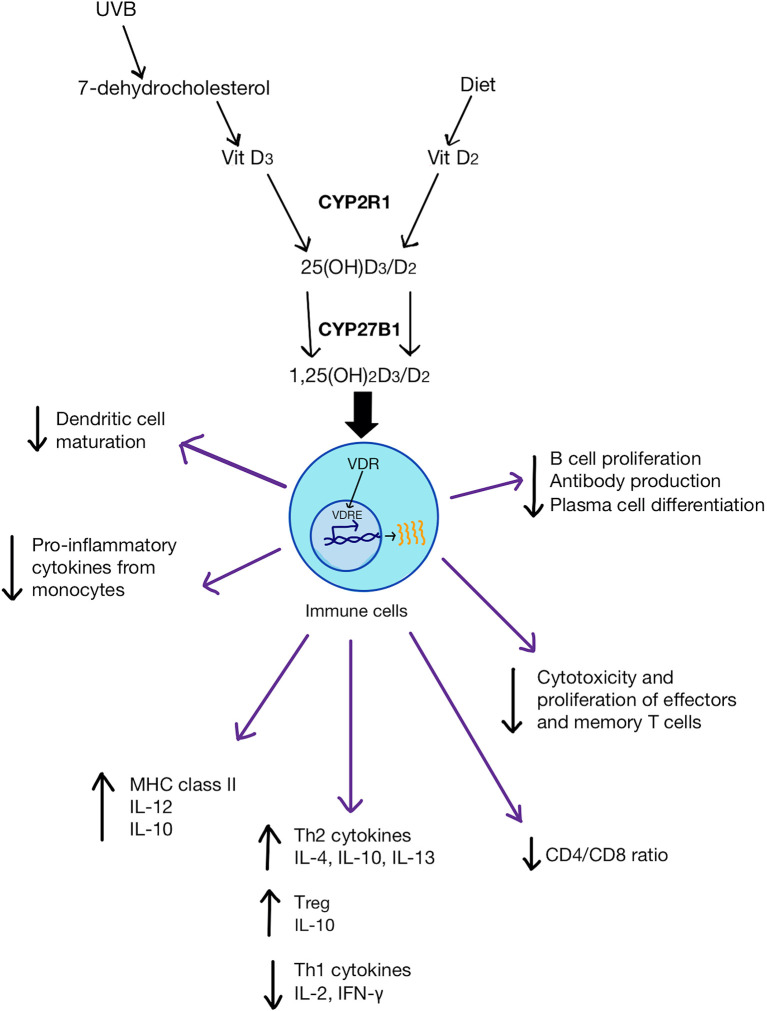
Figure 1.
Vitamin D (both D3 and D2) metabolic pathway and its physiological impact on immune cells. D3 is synthesized from either 7-dehydrocholesterol from the skin via UVB activation or through the diet. D2 is obtained from the diet. CYP2R1 enzyme converts D3/D2 to 25(OH)D3/D2 in the liver. CYP27B1 transforms 25(OH)D3/D2 into 1,25(OH)2D3/D2 in the kidneys. 1,25(OH)2D binds to VDR in immune cells which then bind to VDRE on genes to change gene expression. 1,25(OH)2D can inhibit dendritic cell maturation, promote monocyte proliferation and differentiation into macrophages. It can also increase anti-inflammatory cytokines and the frequency of Tregs, as well as reduce pro-inflammatory Th1 cytokines. 1,25(OH)2D can also reduce the ratio of CD4/CD8 and inhibit pro-inflammatory T cell differentiation and suppress antibody production by B cells.