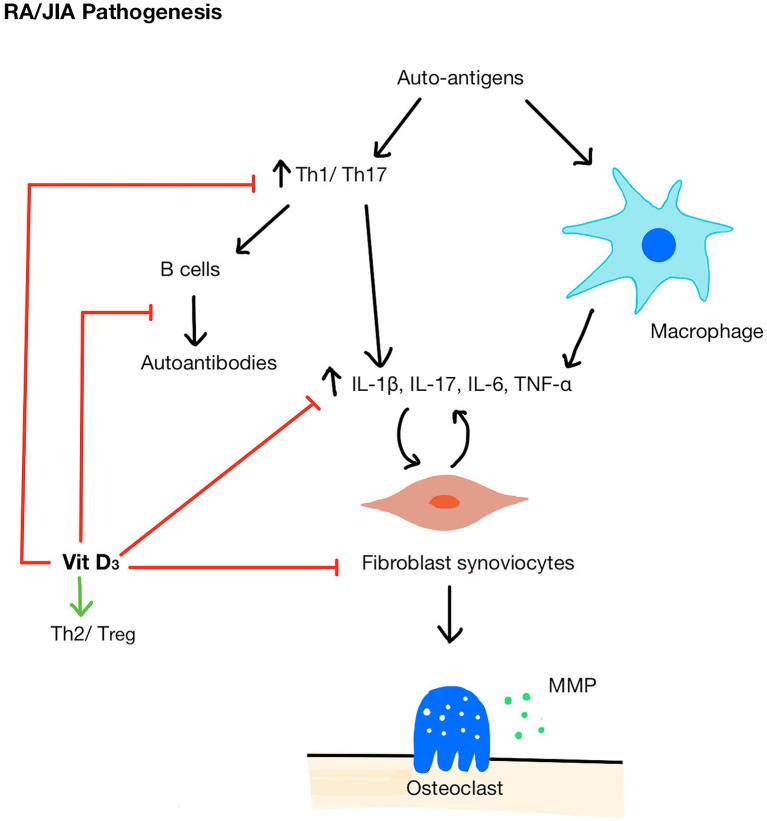
Figure 2.
Pathogenesis of RA/JIA and mechanisms of vitamin D acting on immune cells. A breakdown in tolerance in RA/JIA leads to increased Th1/Th17 cells and promotes macrophages to produce pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-17, IL-6, TNF-α) which in turn stimulates fibroblast synoviocyte proliferation. Synoviocytes then activate osteoclasts and secrete MMPs which break down bone and cartilage. Vitamin D shifts the balance of Th cells from Th1/Th17 to Th2/Treg, inhibit B cells and autoantibody production, reduces pro-inflammatory cytokines, and inhibits synoviocyte proliferation. MMP, matrix metallopeptidase.