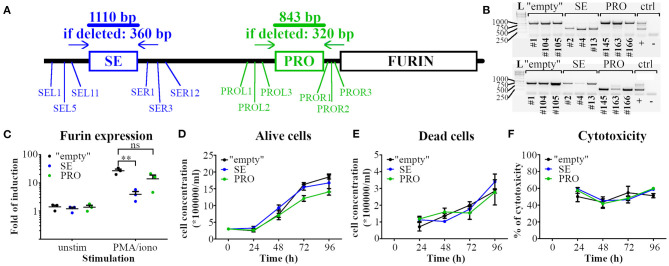
Figure 2.
Deletion of p300 binding enrichment site upstream of Furin gene impairs the activation-induced Furin expression in T cells. (A) Schematic representation of the deletion strategy of the high p300-binding areas at the putative super-enhancer (SE) and the promoter region (PRO) of the Furin gene (FURIN). gRNAs targeting the upstream (L) and downstream (R) sequence of the p300 binding areas were designed, cloned to Cas9 expression vectors and transfected in pairs (SEL and SER or PROL and PROR) into EL-4 mouse thymoma cells. (B) Deletion efficiency in EL-4 cell clones was assessed with PCR using primer pairs outside of the targeted deletion area. Three independent EL-4 cell clones with full deletion of SE (above) or PRO (below) region or transfected without gRNA (“empty”) were kept for further investigations. A cell clone with heterozygous PRO region deletion was used for PCR control (control lane +). L = 1kb DNA ladder. (C) “Empty,” SE area deleted (SE) and PRO region deleted (PRO) EL-4 clones were left unstimulated or stimulated with PMA and ionomycin for 6 h and Furin mRNA expression was examined with qRT PCR. Normalized Furin expressions were compared using Student's t-tests (**p < 0.01). (D–F) Viability and proliferation of EL-4 cell clones. “Empty,” SE, and PRO clones were cultured under identical conditions, and the number of alive (D) and dead (E) cells was determined manually for 96 h. Additionally, samples from each EL-4 clone culture were taken daily and cytotoxicity was determined using LDH assay (F). Data are shown as means ± SEM (n = 3/genotype). (D–F) The experiment was repeated three times with similar results).