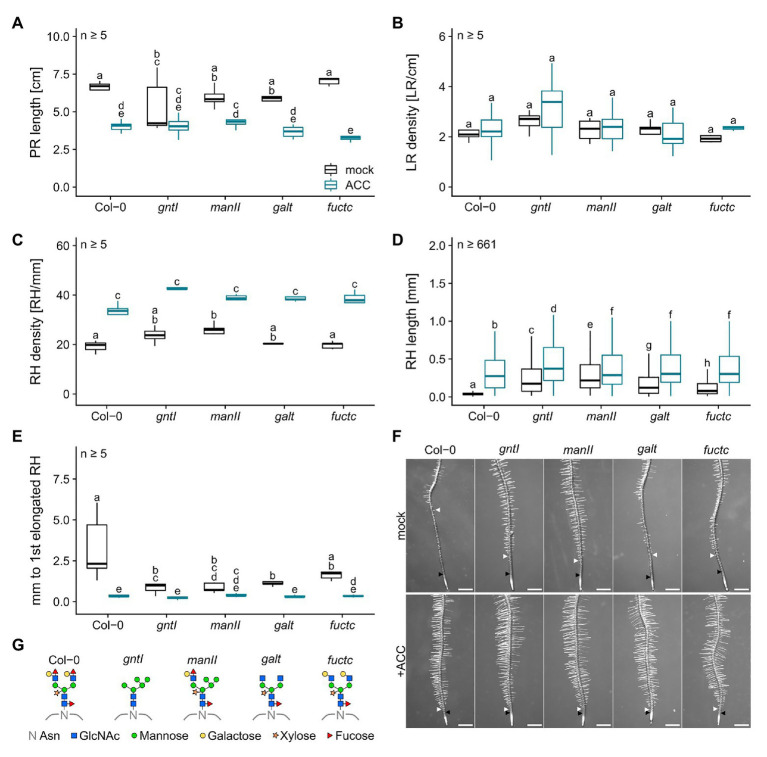
Figure 2.
Roots compromised in complex N-glycan modification respond wild type-like to ACC. (A) Primary root length, (B) lateral root density, (C) root hair density, (D) root hair length, and (E) distance between first general and first partially elongated root hair of N-glycosylation mutants and wild-type plants cultivated for 8 days on mock (black boxes) or 100 nM ACC (blue boxes). Letters indicate significant differences between groups [p ≤ 0.05; (A–C,E) two-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc test; (D) Kruskal-Wallis test, FDR corrected via Benjamini-Hochberg]. (F) Pictures of wild type (Col-0) and N-glycosylation mutant root tips. Black arrows indicate the first general root hair while white arrows point to the first partially elongated root hair. Scale bars: 500 μm. (G) N-glycan structures of the mutants tested. PR, primary root; LR, lateral root; RH, root hair; Asn, Asparagine; GlcNAc, N-acetylglucosamine.