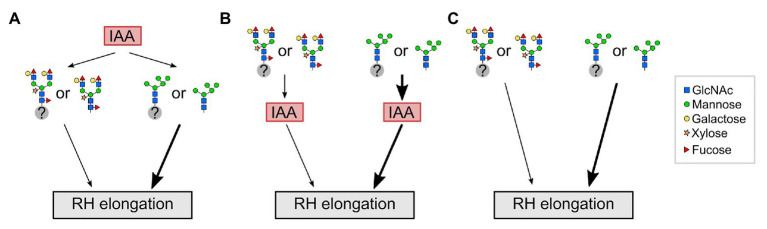
Figure 5.
Potential interplay between auxin (IAA) and complex N-glycosylation during RH elongation. (A) In wild-type roots with fully matured complex N-glycans, a (group of) yet unknown N-glycosylated factor(s) (gray circle with question mark) or free N-glycans act downstream of auxin (indole acetic acid, IAA) to regulate RH elongation. An impairment of fully matured N-glycans in complex glycosylation mutants (depicted by N-glycans as they appear in gntI) results in exaggerated elongation of RHs (thick black arrow). (B) Complex N-glycosylation acts upstream of IAA to regulate RH elongation. An impairment of fully matured N-glycans in complex glycosylation mutants results in exaggerated RH elongation by enforcing the auxin output. (C) Complex N-glycosylation acts independent of IAA on RH elongation. RH, root hair; GlcNAc, N-acetylglucosamine.