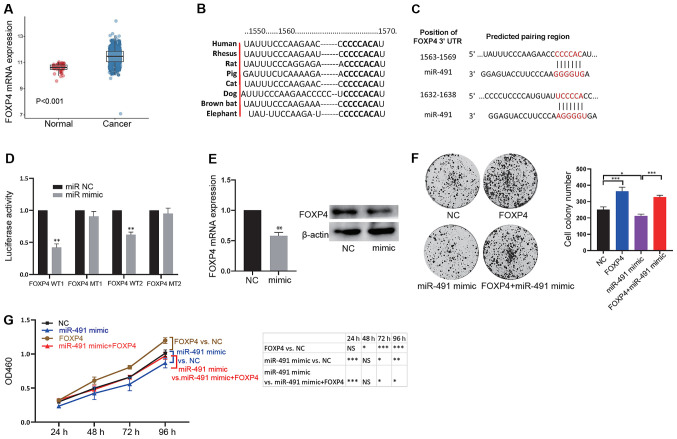
Figure 3.
miR-491 functionally targets FOXP4. (A) FOXP4 expression was significantly increased in cancer tissues compared with normal tissues. (B) The binding site between FOXP4 and miR-491 is conserved across different species. (C) Potential binding sites between the 3′-UTR in FOXP4 with miR-491. (D) miR-491 mimic decreased luciferase activity of the vector containing WT binding sites in 293T cells. *P<0.05 vs. miR NC. (E) miR-491 decreased FOXP4 mRNA (left) and protein (right) expression levels. **P<0.01 vs. NC. (F) SW620 cells were divided into four groups: NC, overexpression of FOXP4 (FOXP4), overexpression of miR-491 (miR-491 mimic), and concurrent overexpression of FOXP4 and miR-491 (FOXP4 + miR-491 mimic). Cell colony formation assays were performed in the different groups of cells: Right, representative figures; left, quantitative analysis. (G) SW620 Cells were divided into four groups: NC, overexpression of FOXP4 (FOXP4), overexpression of miR-491 (miR-491 mimic), and concurrent overexpression of FOXP4 and miR-491 (FOXP4 + miR-491 mimic). Cell Counting Kit-8 assays were performed in the different groups of transfected cells. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, as indicated. Experiments were repeated three times. miR-491, microRNA-491; FOXP4, forkhead box P4; UTR, untranslated region; NC, negative control; WT, wild-type; MT, mutant; OD, optical density.