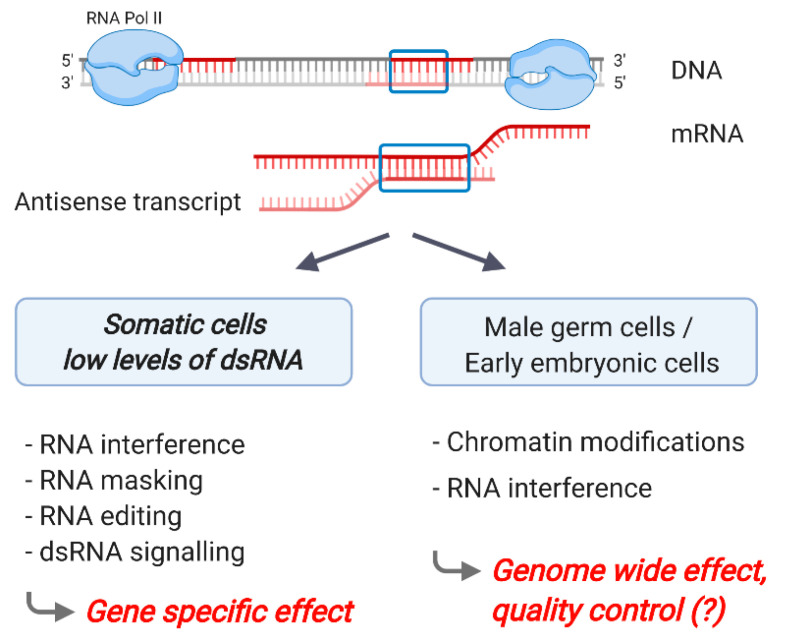
Figure 2.
Double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) formation from sense–antisense transcripts. Natural antisense transcripts are processed and potentially reach the cytoplasm, where they interact with the sense transcript. In somatic cells, the level of sense–antisense hybrids is low, and there is no evidence of ADAR editing, for example, nor is dsRNA immune signaling triggered. Various mechanisms (RNA interference, RNA masking, RNA editing and dsRNA signaling) are potentially triggered by the dsRNA, depending on the cellular context. In male germ cells and during early embryogenesis, sense–antisense dsRNA formation may play a general, system-relevant role. Figure created with Biorender.com.