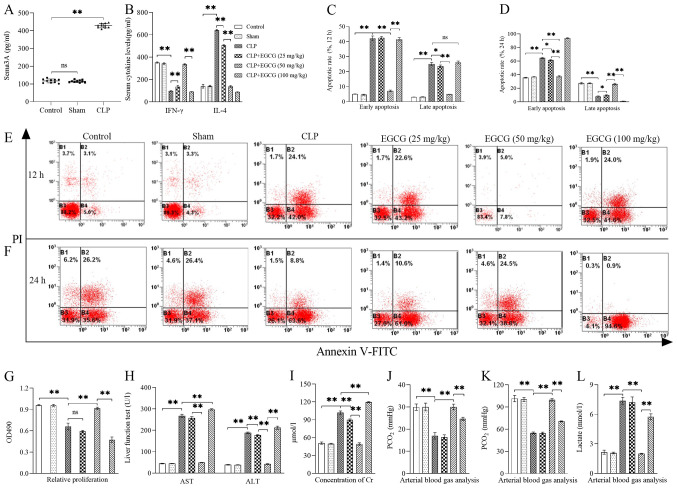
Figure 1.
Treatment with EGCG improves sepsis-induced T cell immunosuppression and MODS. (A) The serum concentration of Sema3A was significantly enhanced in CLP-induced sepsis (n=10). (B) Serum concentrations of IFN-γ and IL-4. Statistical analysis and representative flow cytometry images of proportions of early and late apoptotic stage CD4+ T cells from (C and E) 12 h to (D and F) 24 h. PI-Annexin V-FITC+ represent early apoptosis, while PI+Annexin V-FITC+ represent late apoptosis. (G) The proliferation of CD4+ T cells. Serum concentrations of (H) AST and ALT, (I) Cr, (J) PCO2, (K) PO2 and (L) Lactate. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation, n=4 per group. One-way ANOVA was performed for data analysis. *P<0.05, **P<0.01. EGCG, (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate; MODS, multiple organ dysfunction syndromes; ns, not significant; CLP, cecal ligation and perforation; AST, aminotransferase; ALT, alanine transaminase; Cr, creatinine; Sema3A, semaphorin 3A.