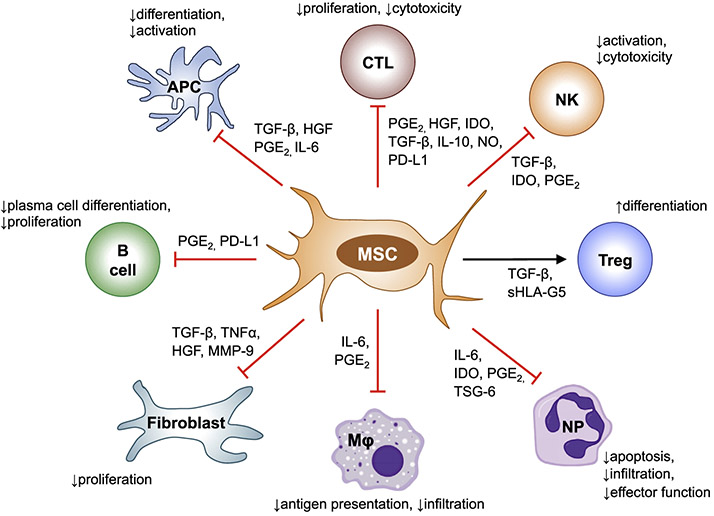
Fig. 1. Immunomodulatory functions of MSCs.
MSCs regulate the immune response via both cell-cell contact and soluble factors. MSCs inhibit the proliferation and function of T cells, limit activation of NK cells, suppress APC differentiation and activation, inhibit B cell proliferation and differentiation into plasma cells, reduce the antigen presenting capacity of macrophages and decrease neutrophil apoptosis, infiltration and effector function. MSC also induce Treg differentiation. Abbreviations: CTL, cytotoxic T cell; NK, NK cell; Treg, regulatory T cell; NP, neutrophil; Mφ, macrophage; APC, antigen-presenting cell; PGE-2, prostaglandin E2; TSG-6, tumor necrosis factor-inducible gene 6 protein; HGF, hepatocyte growth factor; IDO, indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-β; IL, interleukin; NO, nitric oxide; PD-L1, programmed death ligand 1; SHLA-G5, soluble human leukocyte antigen-G; TNFα, tumor necrosis factor α; MMP-9, matrix metallo-peptidase 9.