Figure 2. Nanotweezers.
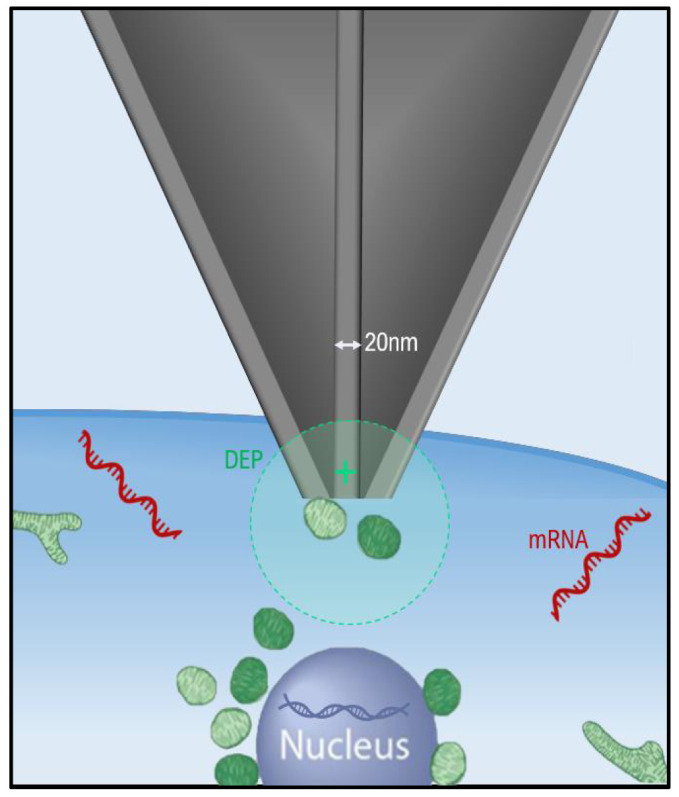
The nanotweezers tip is inserted into a cell and then application of an alternating current (A.C.) results in a localised electric field that traps biomolecules at the probe tip through dielectrophoretic (DEP). This DEP force is strong enough to capture nucleic acids and mitochondria in solution. Once captured the molecules can then we withdrawn from out of the cell of interest with the removal of the nanotweezers and transferred to a collection vessel. The applied DEP force is reversible and turning off the A.C. results in the release of the captured biomolecules.
