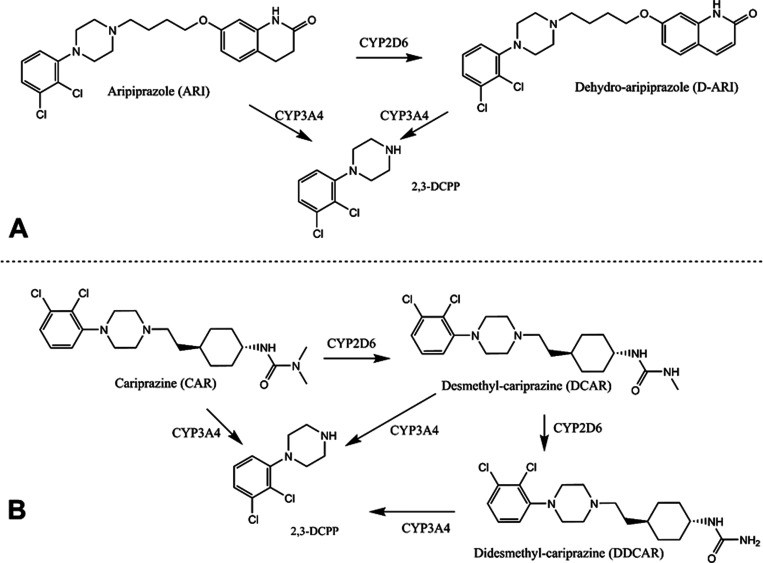
Figure 1.
Simplified metabolism of ARI and CAR. (A) CYP2D6 catalyzes ARI’s dehydrogenation to generate D-ARI. Both ARI and D-ARI can undergo N-dealkylation by CYP3A4 to generate 2,3-DCPP. (B) CYP2D6 catalyzes the conversion of CAR into DCAR, which is then converted into DDCAR. CAR, DCAR, and DDCAR can undergo N-dealkylation to generate 2,3-DCPP.