Figure 8.
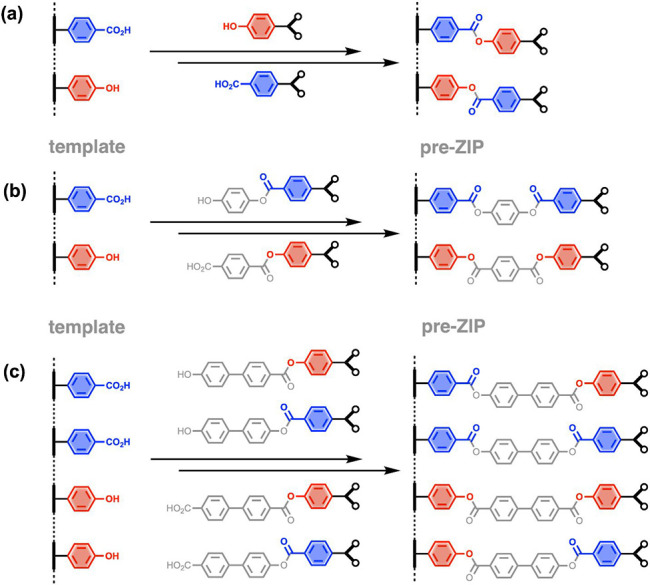
Information transferred from the parent to the daughter strand can be programmed by using base pairs connected by traceless linkers (gray). (a) Reciprocal replication. A base pair formed by the direct attachment of benzoic acid and phenol units results in a complementary copy of the template. (b) Direct replication. Connecting two identical bases via a symmetric linker results in an identical copy of the template after cleavage of all of the ester bonds to release the linker. (c) Replication with mutation. Isosteric linkers can be used to introduce mixtures of symmetric and unsymmetric base pairs, which result in simultaneous direct and reciprocal copying.
