Figure 10.
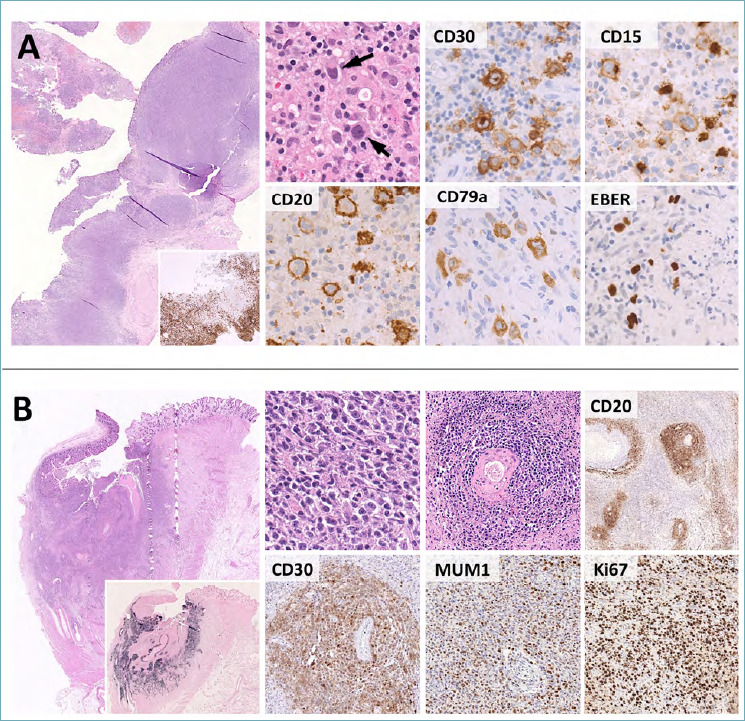
Histological features of EBVMCU and monomorphic PTLD. (A) EBVMCU is an ulcerated, sharply demarcated lymphoid lesion with a band-like CD3-positive T-cell infiltrate at the base (large box, insert). Hodgkin/Reed Sternberg-like cells are characteristically present (high power picture, arrow) and express CD30, multiple B-cell markers (e.g. CD20, CD79a), MUM1 and EBER. CD15 is present in subsets of cases. These features need to be distinguished from cHL, whose primary involvement of the GI tract is extremely rare. (B). The differential diagnosis of EBVMCU encompasses various EBV-positive LPDs, including monomorphic PTLD. This consists of sheets of atypical blasts with variable histological features (the case reported here has lymphomatoid granulomatosis-like features with marked angiotropism). CD20, CD30 and MUM1 are typically expressed, EBER positivity is strong and diffuse (large box, insert) and the Ki67 index is high. (H&E, immunoperoxidase stain; original magnification 2x, 10x, 20x and 40x).
