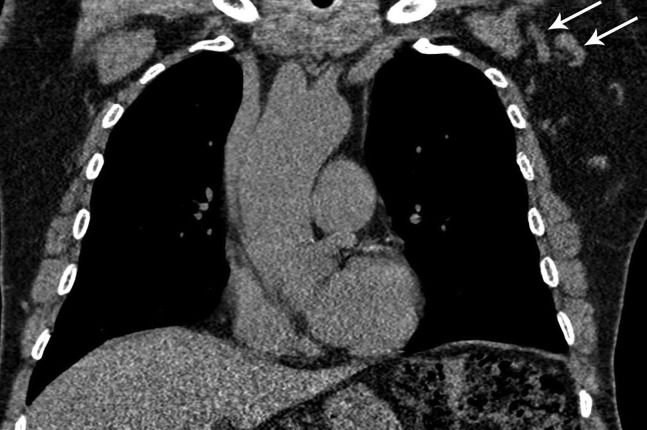
Fig 3.
A 64-year-old man, with a 30-pack-year smoking history, presented for lung cancer screening chest CT, 10 days after receiving his first dose of the Moderna coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccine in the left deltoid muscle. Low-dose non-contrast-enhanced CT coronal imaging showed asymmetric mild enlargement of several left axillary lymph nodes (arrows). The findings were otherwise negative for suspicious pulmonary nodules. Given recent COVID-19 vaccination, the case was interpreted as Lung-RADS category 2. The axillary lymphadenopathy was reported as a “potentially significant finding” using the Lung-RADS “S” modifier. The recommendation was to return to routine annual lung cancer screening. No additional imaging evaluation for the isolated axillary lymphadenopathy was recommended, unless it increases or persists for more than 6 weeks, at which point ultrasound may be considered.