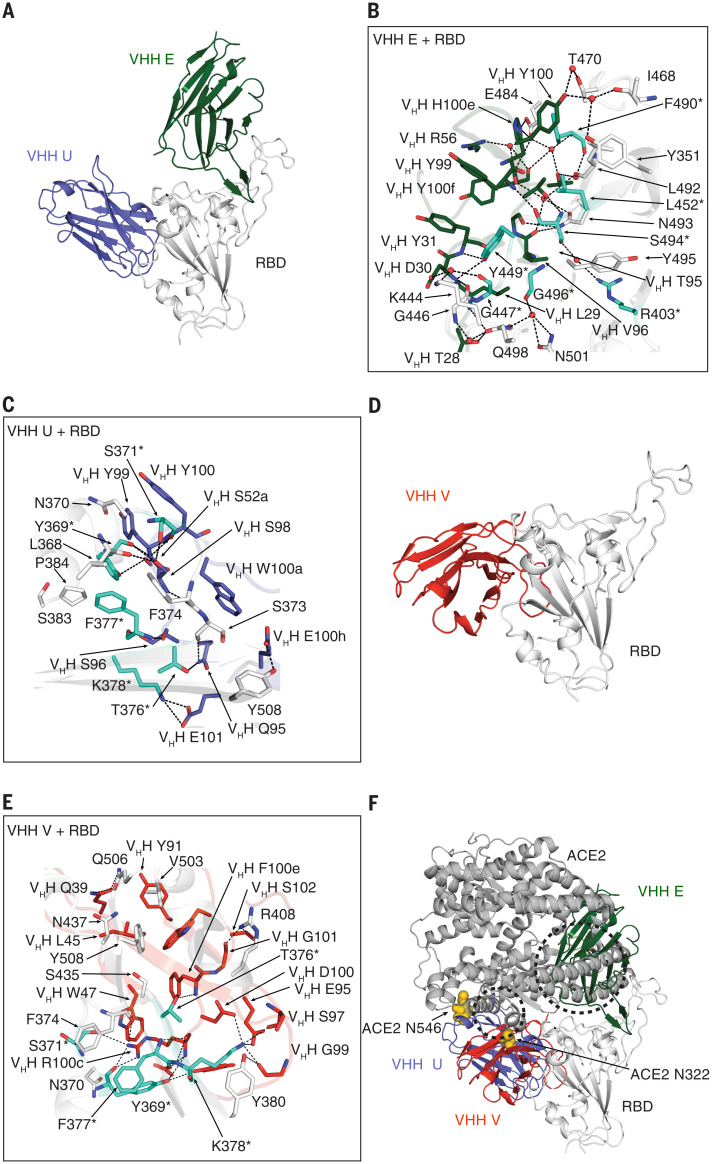
Fig. 2. X-ray crystallography defines the binding sites of neutralizing VHHs on the SARS-CoV-2 RBD.
(A to C) Crystal structure of SARS-CoV-2 spike RBD in complex with VHH E and VHH U at 1.87 Å (A) and detailed interaction interface of RBD (in white) with VHH E (B) and RBD with VHH U (C), respectively. (D and E) Crystal structure of SARS-CoV-2 spike RBD in complex with VHH V at 2.55 Å (D) and detailed interaction interface of RBD with VHH V (E). Escape mutants (see Fig. 5 and tables S5 to S8) in the RBD are highlighted in teal and labeled with asterisks. (F) Overview of binding sites of three neutralizing nanobodies on the RBD and their overlap with ACE2, based on PDB ID 6M0J (67). Steric clashes with VHH E are indicated within the dashed circles. N-glycans at N322 and N546 of ACE2 are depicted as yellow spheres. All structural analyses of VHH U and VHH E in complex with RBD were based on one of the two copies in the asymmetric unit with closer alignment to the localized reconstructions of VHH E with RBD and VHH VE with RBD using cryo-EM. Single-letter abbreviations for the amino acid residues are as follows: A, Ala; C, Cys; D, Asp; E, Glu; F, Phe; G, Gly; H, His; I, Ile; K, Lys; L, Leu; M, Met; N, Asn; P, Pro; Q, Gln; R, Arg; S, Ser; T, Thr; V, Val; W, Trp; and Y, Tyr.