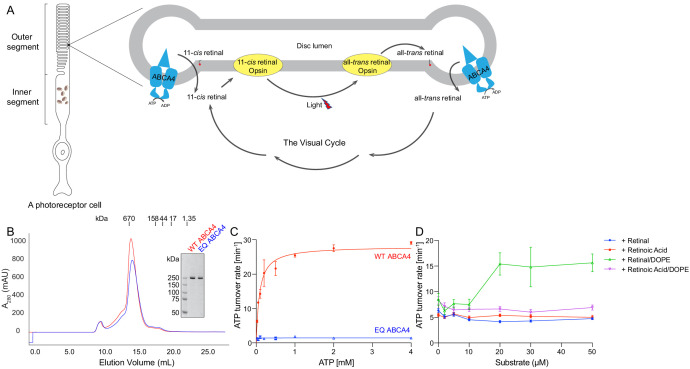
Figure 1. Biochemical characterization of ABCA4.
(A) An illustration showing a rod photoreceptor cell and a zoomed-in view of the outer segment disc, where ABCA4 is located. ATP-hydrolysis enables ABCA4 to transport all-trans retinal and 11-cis retinal from the disc lumen into cytosol. (B) Size exclusion profile of purified wild-type (WT) ABCA4 and the E1087Q/E2096Q mutant (EQ). (C) Basal ATPase activity measured in 0.06% digitonin at 28°C. Data points represent the means and standard deviations (SDs) of three measurements. The WT ABCA4 has a Km of 0.08 ± 0.01 mM and specific turnover rate of 28.1 ± 0.7 ATP per minute, corresponding to a maximal ATPase activity of 112.5 ± 2.8 nmol/mg/min. (D) The ATPase activity of purified ABCA4 as a function of all-trans retinal or all-trans retinoic acid in the presence or absence of 0.1 mg/mL 1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine (DOPE) and 100 µM ATP. Data points represent the means and SDs of three measurements from the same protein preparation.