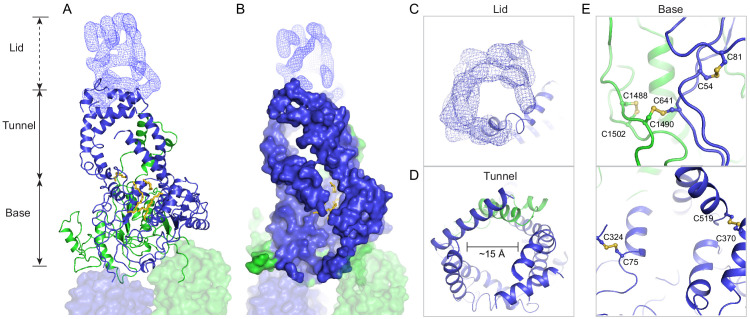
Figure 3. A three-tiered structure of the exocytoplasmic domains (ECDs).
(A) Ribbon and (B) surface representation of the ECDs, together with the electron microscopy (EM) density of the lid region. Bound detergents and lipids are shown as yellow sticks. (C) A luminal view of the lid; the EM density is shown as blue mesh. (D) A cross section of the tunnel region. (E) The ECDs are stabilized by inter- and intra-domain disulfide bonds.
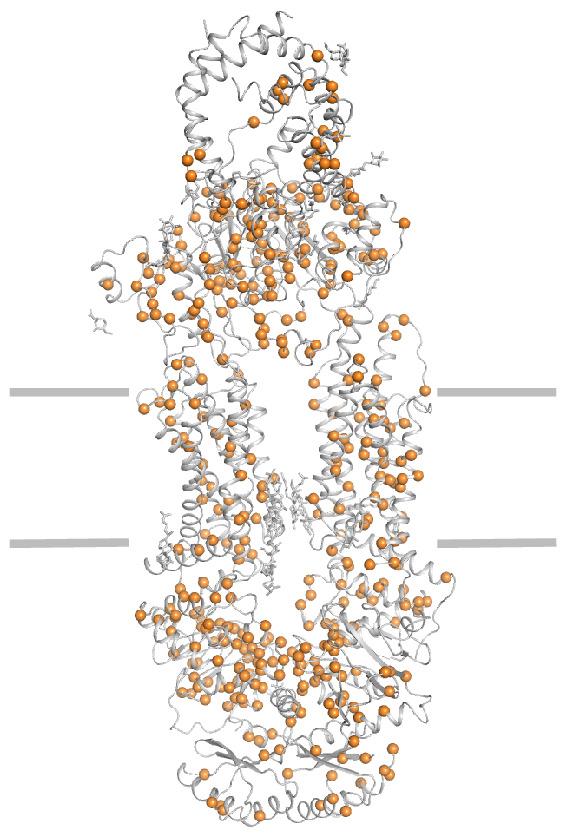
Figure 3—figure supplement 1. Disease-causing mutations (orange) are widely distributed throughout the structure.