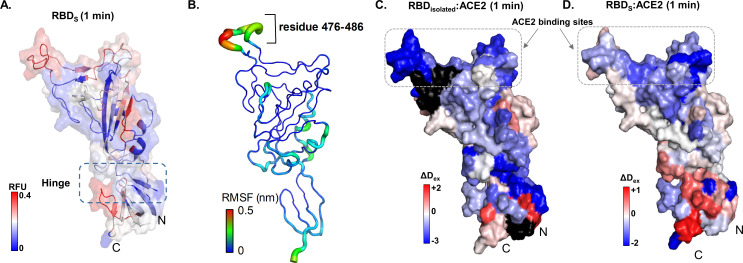
Figure 3. Map of receptor binding domain (RBD)isolated:angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) interactions.
(A) Relative fractional deuterium uptake values at t = 1 min for RBD (314–547) of spike (S) protein (RBDS) mapped onto the structure of RBD extracted from S protein model (see Supplementary file 1: Table S2). High and low exchanging regions are represented as shown in key, and regions with no coverage are shown in black. (B) The root mean square fluctuation (RMSF) values of backbone atoms on the RBD showing residues with high RMSF (476–486) as per key. Differences in deuterium exchanged between RBDisolated:ACE2 complex and free RBDisolated (C) and RBDS:ACE with free RBDS (D) at 1 min of deuterium labeling are mapped onto the structure of RBD. Protection from deuterium uptake and increases in exchange are indicated in blue and red, respectively. Regions with no peptide coverage are in black. RFU: relative fractional deuterium uptake.