Figure 1.
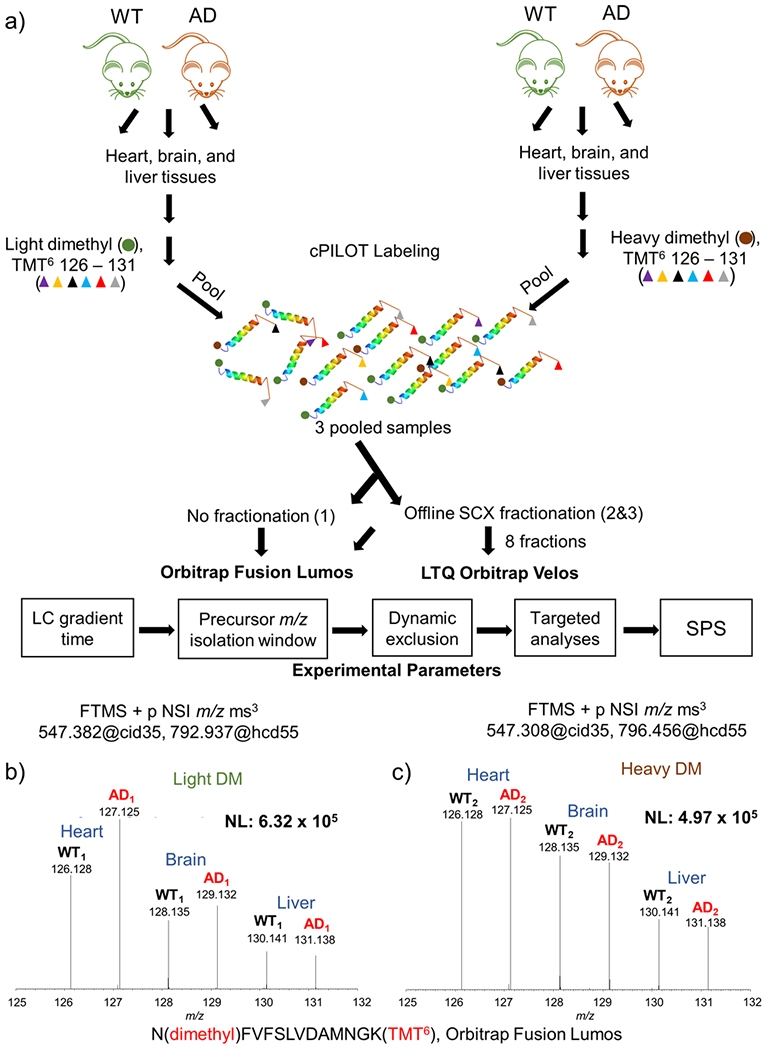
Experimental workflow and sample data. (a) Protein (100 μg) was extracted from brain, heart, and liver tissues from 14-month-old APP/PS-1 (N = 6) and wild-type controls (N = 6). Peptides generated from protein digestion were labeled via cPILOT, pooled, and separated by off-line SCX fractionation and reversed-phase HPLC. Fractions were analyzed on either an Orbitrap Fusion Lumos or LTQ Orbitrap Velos MS. Experimental parameters such as LC, precursor m/z isolation window, dynamic exclusion, targeted analyses, and SPS were evaluated and optimized on the Fusion Lumos. Reporter ions (i.e., 126–131) corresponding to N(dimethyl)-FVFSLVDAMNGK(TMT6) were detected on the Orbitrap Fusion Lumos. (b) Light and (c) heavy dimethylated peptides were detected in both phenotypes, and all tissue types and correspond to malate dehydrogenase.
