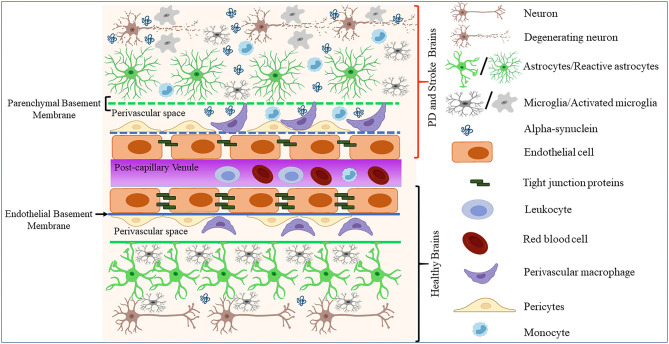
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of how pathological α-synuclein-accumulation occurring in PD or stroke can disrupt the physiological homeostasis of the BBB by affecting its diverse components. The BBB is composed of microvascular endothelial cells, pericytes, astrocytes, and BM components deposited by ECs (endothelial BM) and astrocytes (parenchymal BM). More recently, perivascular macrophages and vessel-associated microglia were found to play a role in the maintenance and repair of BBB whose disruption is detected in various neurological disorders including stroke and PD. This could result in BM damage (dotted lines), downregulation of TJ proteins, abnormal accumulation, and spreading of toxic forms of proteins such as α-synuclein, activation of glial cells and PVMs, and infiltration of peripheral leukocytes and monocytes, leading to neuronal degeneration.