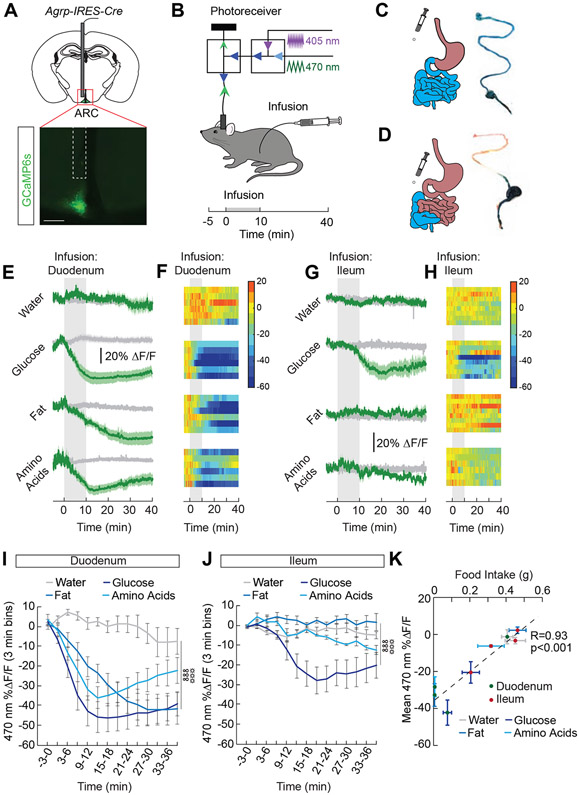
Figure 1. Site-specific detection of macronutrients in the intestine by AgRP neurons.
(A) Representative image showing GCaMP6s expression in AgRP neurons of AgRP-IRES-Cre mice. Scale bar, 200 μm. (B) Schematic showing the dual-wavelength fiber photometry setup used to monitor AgRP neuron activity during infusions into the intestine. Infusates were delivered over 10 min (1 mL, 0.1 mL/min). (C) Schematic and representative image of a duodenal infusion. (D) Schematic and representative image of an ileal infusion. (E) Average ΔF/F of GCaMP6s signals in AgRP neurons of food-restricted mice with intra-duodenal (ID) infusions of water, glucose (2/3 kcal), fat (1 kcal), and amino acids (1 kcal) (n=6/group). Signals are aligned to the start of the infusion. Green, 470-nm calcium signal; grey, 405-nm control signal. Dark lines represent means and lighter shaded areas represent SEM. (F) Heat maps reporting ΔF/F of the 470-nm signal of the recordings in individual mice in (E). (G) Average ΔF/F of GCaMP6s signals in AgRP neurons of food-restricted mice with intra-ileal (II) infusions of water, glucose (2/3 kcal), fat (1 kcal), and amino acids (1 kcal) (n=6-8/group). (H) Heat maps reporting ΔF/F of the 470-nm signal of the recordings in individual mice in (G). (I) Mean ΔF/F of the 470-nm signal (3-min bins) in AgRP neurons with ID infusions of macronutrients in (E) (n=6/group, two-way repeated measures ANOVA, p<0.001). (J) Mean ΔF/F of the 470-nm signal (3-min bins) in AgRP neurons with II infusions of macronutrients in (G) (n=6-8/group, two-way repeated measures ANOVA, p<0.001). (K) Correlation between food intake and mean ΔF/F in AgRP neurons following intestinal infusion of macronutrients (n=6-9/group, Pearson’s correlation, p<0.001). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM, t-tests and post-hoc comparisons: ANOVA interaction: ∞∞∞p<0.001; ANOVA main effect of group: ☼☼☼p<0.001. See also Figures S1-S4.