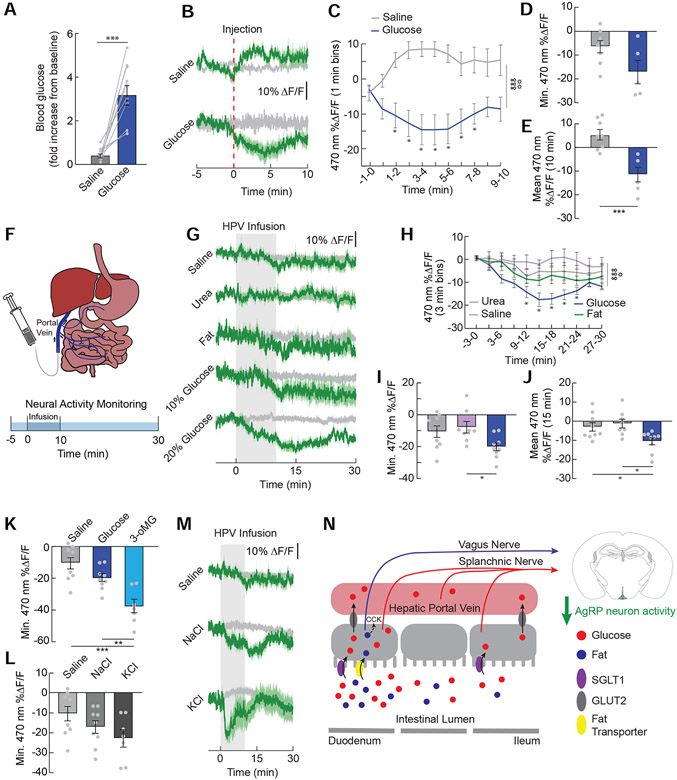
Figure 5. AgRP neurons detect glucose in the hepatic portal vein.
(A) Increase in blood glucose levels 10 min post-injection of IP glucose (2 g/kg) or equi-osmotic NaCl (n=10/group, paired t-test, p<0.001). (B) Average ΔF/F of GCaMP6s signals in AgRP neurons of food-restricted following IP injection of saline or glucose. Signals are aligned to the start of the infusion. Green, 470-nm calcium signal; grey, 405-nm control signal. Dark lines represent means and lighter shaded areas represent SEM. (C) Mean ΔF/F of the 470-nm signal (1-min bins) in AgRP neurons during IP injections of saline or glucose (n=5-8/group, two-way repeated measures ANOVA, p<0.001). (D) Minimum ΔF/F of the 470-nm signal during IP injections of solutions in (J) (n=5-8/group, unpaired t-test, p=0.06). (E) Mean ΔF/F of the 470-nm signal from 0 to 10 minutes during IP injections of solutions in (J) (n=5-8/group, unpaired t-test, p<0.001). (F) Nutrients were infused into the hepatic portal vein (HPV) and AgRP neuron activity was monitored. (G) Average ΔF/F of GCaMP6s signals in AgRP neurons of food-restricted mice during HPV infusions of saline, urea (6.7%), fat (8% Intralipid, 0.4 kcal), 10% glucose (0.2 kcal), and 20% glucose (0.4 kcal). (H) Mean ΔF/F of the 470-nm signal (3-min bins) in AgRP neurons with HPV infusions of saline, urea, fat, or 20% glucose (n=8-9/group, two-way repeated measures ANOVA, p<0.001). (I) Minimum ΔF/F of the 470-nm signal following HPV infusions of saline, urea, or 20% glucose (n=8-9/group, one-way ANOVA, p<0.05). (J) Mean ΔF/F of the 470-nm signal from 0-15 min following infusions of saline, urea, or 20% glucose (n=8-9/group, one-way ANOVA, p<0.05). (K) Minimum ΔF/F of the 470-nm signal following HPV infusions of saline, glucose, or 3-oMG (n=7-9/group, one-way ANOVA, p<0.001). (L) Minimum ΔF/F of the 470-nm signal following HPV infusions of saline, 3.6% NaCl, or 2.2% KCl (n=7-9/group, one-way ANOVA, p=0.09). (M) Average ΔF/F of GCaMP6s signals during HPV infusions of saline, NaCl (3.6%), or KCl (2.2%). (N) Model depicting our findings on the gut-brain signaling pathways necessary for the inhibition of AgRP neurons by fat and glucose. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM, ns p>0.05, t-tests and post-hoc comparisons: *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001; ANOVA interaction: ∞∞∞p<0.001; ANOVA main effect of group: ☼p<0.05, ☼☼p<0.01.