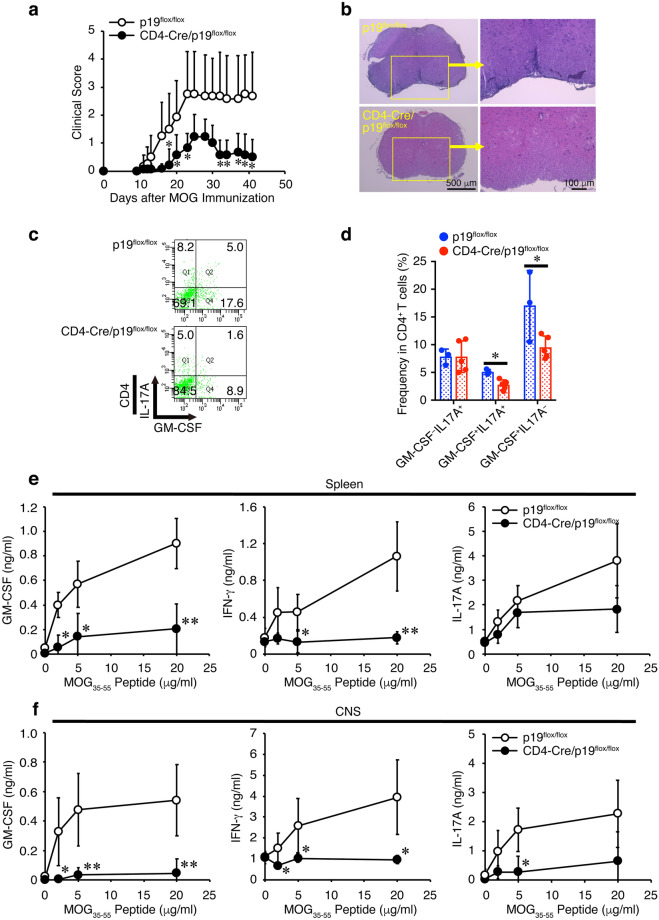
Figure 2.
CD4+ T cell-specific conditional p19-deficient mice show alleviated EAE with reduced frequency of GM-CSF+CD4+ T cells in the CNS. Control p19flox/flox mice or CD4+ T-cell-specific conditional 19-deficient (CD4-Cre/p19flox/flox) mice were immunized with MOG35-55 peptide and their clinical scores were monitored with time (a). On day 14, spinal cords and brains were harvested, and the CNS was histopathologically analyzed with H&E staining. Representative images are shown (b). On day 41, mononuclear cells were isolated from the CNS, and intracellular cytokine staining was performed after restimulation with PMA and ionomycin. Representative dot plots of GM-CSF and IL-17A in CD4+ T cells are shown (c). Average frequencies of respective CD4+ T cells were calculated and compared (d). Response to the recall antigen MOG35-55 peptide was examined using spleen cells (e) and mononuclear cells infiltrating the CNS (f) on day 14. The culture supernatants were analyzed via ELISA for cytokine production as indicated. Data are shown as mean ± SD (n = 3–7) and are representative of two independent experiments. P values were determined using unpaired, two-tailed Student’s t-test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.