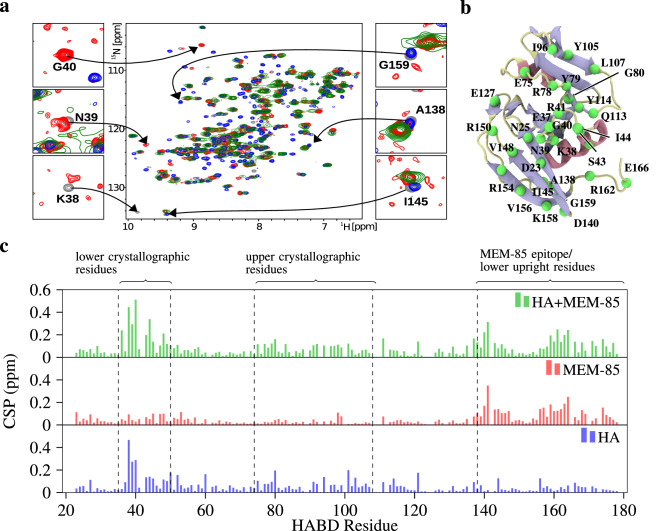
Figure 4.
NMR confirms the simultaneous binding of scFv MEM-85 and hyaluronate to CD44-HABD. (a) 2D N/H HSQC spectra are shown for free N-CD44-HABD (grey), N-CD44-HABD in complexes with hyaluronate hexamer (threefold molar excess; blue), scFv MEM-85 (twofold molar excess; red), and both scFv MEM-85 (twofold molar excess) and hyaluronate hexamer (threefold molar excess; green). Details of the signals are shown for selected residues from the hyaluronate-perturbed (left) and antibody-perturbed (right) regions of CD44-HABD. (b) Illustration of the CD44-HABD (PDB:1UUH), highlighting the residues mentioned in the main text. From the residues, only the atom is depicted (green). Coloring of the protein is based on secondary structure, such that coils are pale, sheets are blue, and helices are red. (c) Histograms of the minimal combined chemical shift perturbation (CSP) versus the protein sequence are shown for N-CD44-HABD in complex with hyaluronate hexamer (blue), scFv MEM-85 (red), and both scFv MEM-85 and hyaluronate hexamer (green).