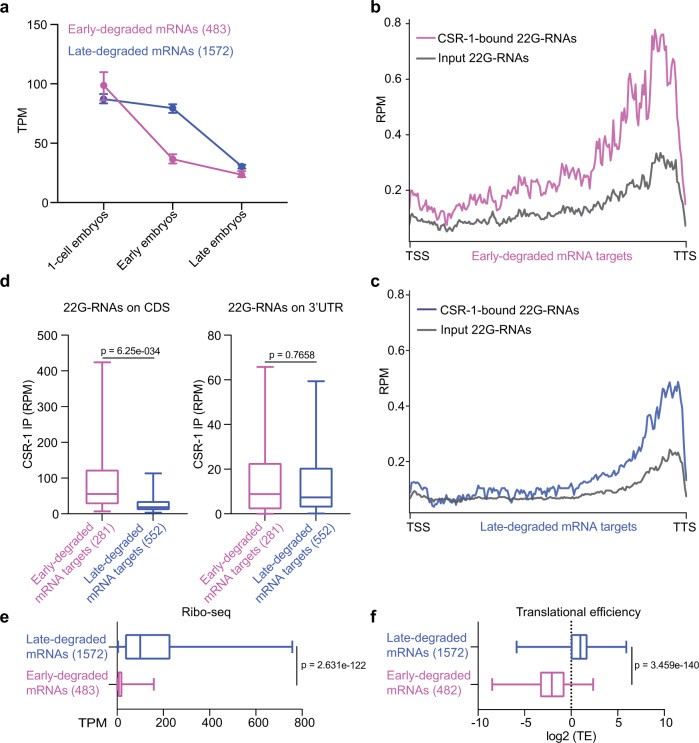
Fig. 5. CSR-1 preferentially targets maternal mRNAs no longer engaged in translation.
a Detection of early- and late-degraded mRNAs by RNA-seq from sorted 1-cell, early and late embryo stages. Data are presented as median and 95% confident interval of normalized read abundances in transcript per million (TPM). The sample size n (genes) is indicated in parentheses. b, c Metaprofile analysis showing normalized 22G-RNA reads (RPM) across early- (magenta) and late-degraded (blue) mRNA targets in CSR-1 immunoprecipitation (IP) or total RNA input (gray). The transcriptional start site (TSS) and transcriptional termination site (TTS) is indicated. The average from three biologically independent replicates is shown. d Box plots showing the abundance of CSR-1-bound 22G-RNAs antisense to coding sequence (CDS) or 3′UTR of early- and late-degraded mRNAs. e Box plots showing the ribosomal occupancy (by Ribo-seq) of early- and late-degraded mRNAs in early embryos. f Median levels and 95% CI of translational efficiency (TE) of early- and late-degraded mRNAs in early embryos. In d–f, the line indicates the median value, the box indicates the first and third quartiles, and the whiskers indicate the 5th and 95th percentiles, excluding outliers. The sample size n (genes) is indicated in parentheses. Two-tailed P value were calculated using the Mann–Whitney–Wilcoxon test. Source data are available online.