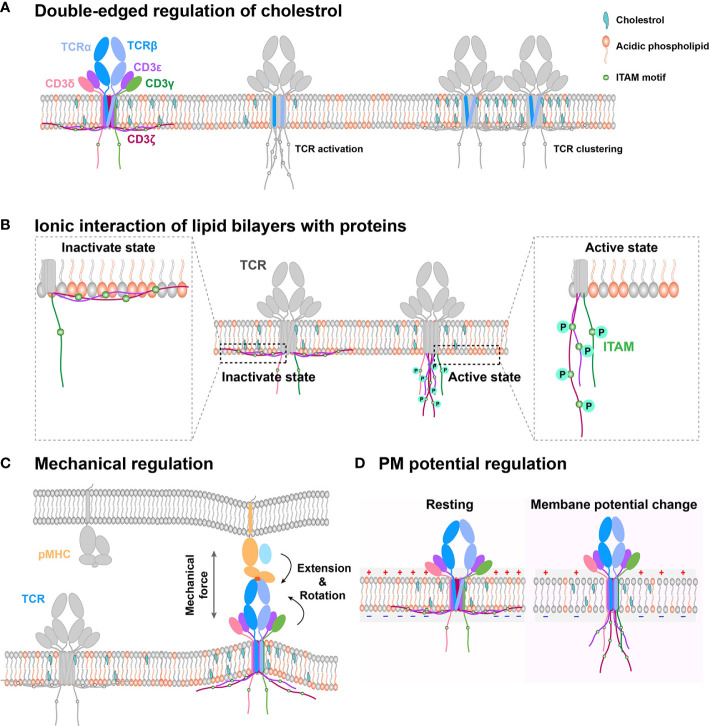
Figure 1.
Schematic models of PM regulation on TCR complex signaling. (A) Double-edged regulation of cholesterol on TCR activation. Cholesterol could directly bind with the TMD of the TCR β chain to keep TCR in an inactive state in the resting T cell. Cholesterol disassociation from the TCR β chain can switch the TCR complex to the activation state. Meanwhile, cholesterol also indirectly mediates TCR clustering, following TCR initial activation. (B) The interaction between negatively charged lipid and basic motif regulates CD3 ITAM motif exposure. TCR cytoplasmic domains contain polybasic regions, which directly interact with the negatively charged lipid in the membrane inner leaflet to embed the ITAM motif in hydrophobic core of the PM in resting cell. The disruption of this interaction can expose the signaling motif to amplify downstream signaling. (C) PM provides a platform to sense outside cues for immune receptors. On this platform, mechanical force regulates TCR/pMHC recognition through conformation change. (D) Electrical potential might directly trigger TCR signaling. Since TCR TMD contains several charged residues, PM potential depolarization might induce TMD titling conformation to further allosterically regulate dissociation of CD3 tails from inner leaflet and activate intracellular downstream signaling.