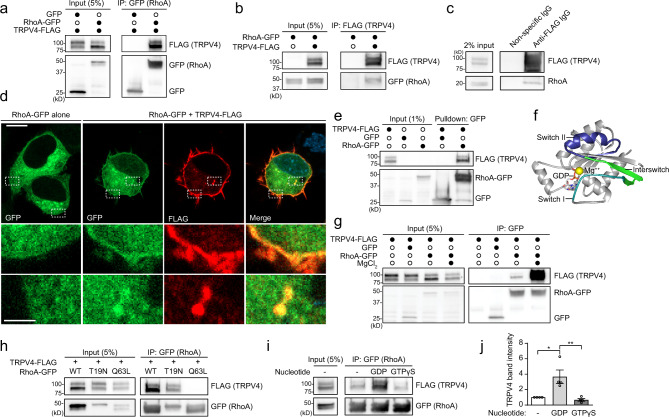
Fig. 1. TRPV4 interacts with GDP-bound RhoA.
a, b MN-1 cells transfected with TRPV4-FLAG and GFP or RhoA-GFP were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-GFP (a) or anti-FLAG (b) antibody. c Stable, inducible TRPV4-FLAG-expressing HEK293T (T-Rex-TRPV4 cells) were treated with tetracycline (15 ng/ml) to induce TRPV4-FLAG expression and subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-FLAG antibody or nonspecific antibody. Endogenous RhoA co-immunoprecipitates with TRPV4. d Immunofluorescence images of MN-1 cells transfected with TRPV4-FLAG and RhoA-GFP demonstrate co-localization of TRPV4 and RhoA at the plasma membrane and within intracellular vesicular structures. Scale bars, 10 and 2.5 µm for inset. e TRPV4-FLAG, RhoA-GFP, and GFP were expressed individually in HEK293T cells and subjected to immunoprecipitation with FLAG or GFP antibody followed by extensive washing. TRPV4-FLAG was eluted with FLAG peptide and then co-incubated with immunopurified RhoA-GFP or GFP. Immunopurified TRPV4 interacts with immunopurified RhoA, suggesting direct interaction. f Structural model of GDP-bound RhoA (PDB: 1FTN) showing the effector-interacting switch I (teal) and II regions (blue), interswitch region (green), magnesium ion (yellow) within the nucleotide-binding pocket, and GDP. g Co-immunoprecipitation of MN-1 cells transfected with TRPV4-FLAG and RhoA-GFP in the presence of EDTA (1 mM in all conditions), which disrupts RhoA nucleotide binding, with or without excess magnesium (10 mM), which stabilizes RhoA nucleotide binding. TRPV4–RhoA interactions are nucleotide dependent. h Co-immunoprecipitation of MN-1 cells transfected with TRPV4-FLAG and WT RhoA-GFP, dominant negative, inactive RhoA-GFP (T19N), or constitutively active RhoA-GFP (Q63L) demonstrates that TRPV4 interacts with WT RhoA and inactive RhoA T19N, but not active RhoA-Q63L. i Co-immunoprecipitation of MN-1 cells transfected with TRPV4-FLAG and RhoA-GFP with excess GDP or unhydrolyzable GTP (GTPγS) demonstrates more efficient interaction between TRPV4 and RhoA in the presence of GDP. j Densitometry of immunoprecipitated TRPV4 band intensity in the presence or absence of GDP or GTPγS; representative blot shown in i. One-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc test, n = 4 independent experiments, *p = 0.013, **p = 0.0066. Data are presented as means ± SEM. Further details regarding the number of times experiments were repeated are presented in “Methods” under “Statistics and reproducibility”.