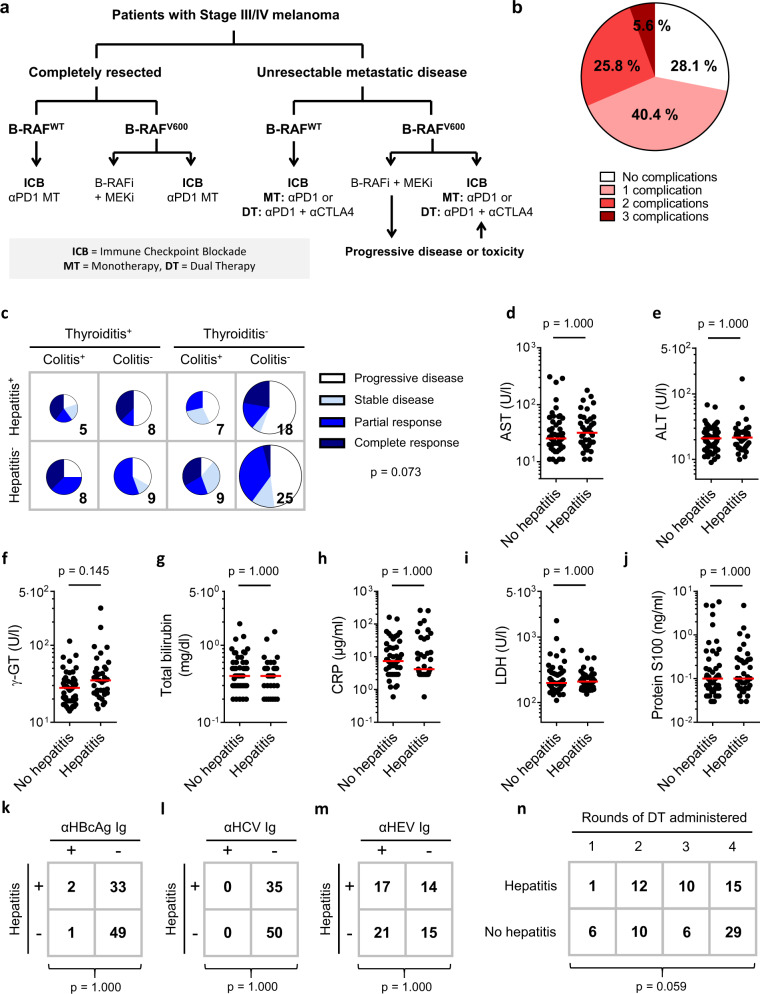
Fig. 1. Individual predisposition to hepatitis after αPD-1/αCTLA-4 treatment.
a Individualised treatment of melanoma is guided by tumour staging, presence of B-RAF mutations and fitness-for-toxicity. b Colitis, hepatitis and thyroiditis are common immune-related complications of dual therapy with Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab; 31.4% of patients experienced two or more of these immune-related adverse reactions (n = 89). c Colitis, hepatitis and thyroiditis occurred independently and were not significantly associated with clinical response (n = 89; F.E). d–h Patients who developed hepatitis of any grade following dual therapy lacked biochemical signs of liver inflammation before treatment. In particular, no clinically meaningful differences in plasma levels of d aspartate transaminase (AST; n = 87; M.W.; Bonferroni-corrected p-value, m = 5), e alanine transaminase (ALT; n = 89; M.W.; Bonferroni-corrected p-value, m = 5), f gamma glutamyl transaminase (γ-GT; n = 89; M.W.; Bonferroni-corrected p-value, m = 5), g total bilirubin (n = 87; M.W.; Bonferroni-corrected p-value, m = 5), or h C-reactive protein (CRP; n = 85; M.W.; Bonferroni-corrected p-value, m = 5) were observed between patients who developed hepatitis and those who did not. Median values are indicated by a red line. i, j Biochemical markers of tumour burden were not different between patients who developed hepatitis and those who did not. i Pre-treatment levels of lactate dehydrogenase (n = 89; M.W.; Bonferroni-corrected p-value, m = 4). Median values are indicated by a red line. j Pre-treatment levels of protein S100 (n = 89; M.W.; Bonferroni-corrected p-value, m = 4). k–m No association was observed between seropositivity for k hepatitis B virus core antigen (HBcAg; n = 85; F.E.; Bonferroni-corrected p-value, m = 3), l hepatitis C virus (HCV; n = 85; F.E.; Bonferroni-corrected p-value, m = 3), or m hepatitis E virus (HEV; n = 67; F.E.; Bonferroni-corrected p-value, m = 3) and development of hepatitis following dual therapy. n No association was observed between rounds of αPD-1/αCTLA-4 administered and development of hepatitis (n = 89; M.W.).