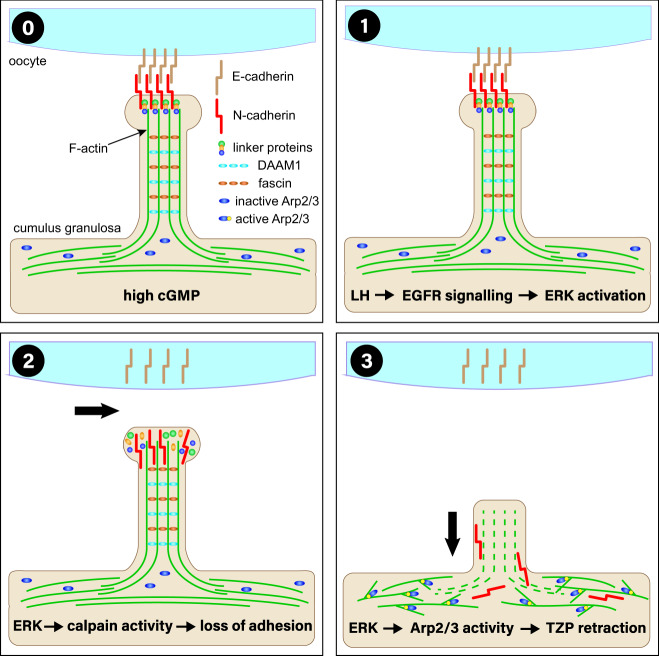
Fig. 7. Model of TZP retraction.
In antral follicles (stage 0), TZPs projecting from the cumulus granulosa cells to the oocyte contain a backbone of linear F-actin together with the formin, DAAM1, and fascin15. N-cadherin (cumulus granulosa) and E-cadherin (oocyte) mediate adhesion between the two cell types. cGMP in the granulosa cells may maintain the TZPs. At the time of ovulation (stage 1), binding of LH to its receptor in the mural granulosa cells triggers release of EGFR ligands, which in turn activates ERK MAP kinase. Active ERK activates calpain (stage 2), which degrades proteins required to maintain N-cadherin at the cumulus granulosa cell membrane, thereby permanently breaking germ-soma contact. Increased activity of the branched chain actin nucleator complex, Arp2/3, which may also be regulated by ERK MAP kinase, reorganizes the actin cytoskeleton (stage 3) leading to a retraction of the TZPs into the granulosa cell body.