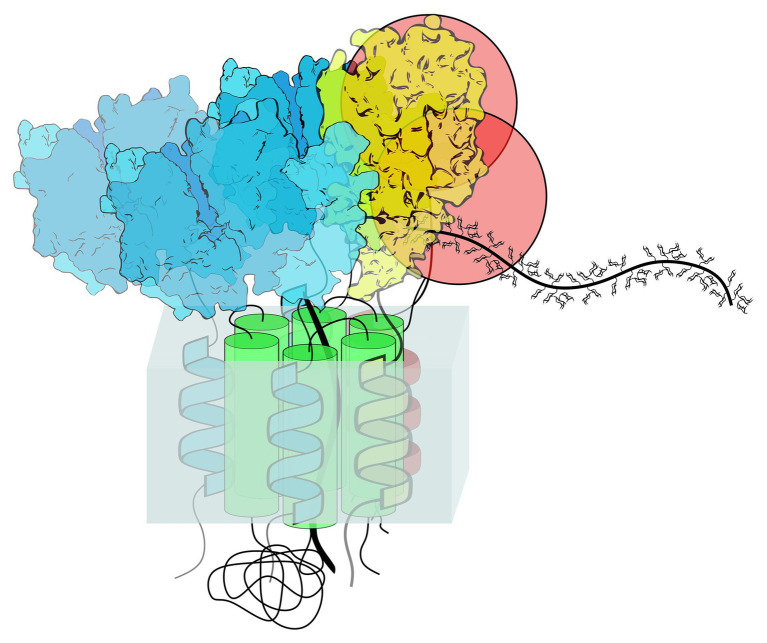
Figure 2.
Hypothetical organization of the xyloglucan synthesizing complex. Seven glycosyltransferases (GTs) have been shown to interact in the Arabidopsis Golgi, forming a multiprotein complex. It is hypothesized that GTs involved in the synthesis of xyloglucan side chains are organized around the CSLC protein that synthesizes the glucan backbone. The CSLC protein has a catalytic domain localized in the cytoplasm, where it adds glucose to the elongating glucan chain, moving the chain into the Golgi lumen through the pore formed by the six TMD helices (green). The other six GTs [three blue xylosyltransferases (XXT1, XXT2, and XXT5), two red galactosyltransferases (MUR3, XLT2), and yellow fucosyltransferase (FUT1)] interact with the TMD of the CSLC protein via their TMDs; in addition, the GTs interact with each other via catalytic domains. The actual crystal structures of XXT1, XXT2, XXT5, and FUT1 (Urbanowicz et al., 2017; Culbertson et al., 2018) are depicted here. Since the structures for MUR3 and XLT2 are not solved, these GTs are depicted as red spheres.