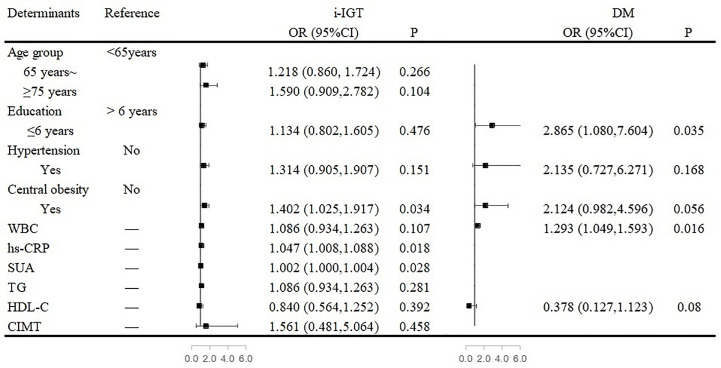
Figure 2.
Associated factors of abnormal glucose regulation in the multivariate analyses in women. Figure 2 showed that central obesity and high levels of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) and serum uric acid (SUA) were independent risk factors for isolated-impaired glucose tolerance (i-IGT). Low education and elevated white blood cell (WBC) count were independent risk factors for diabetes mellitus (DM) among women.