Figure 3.
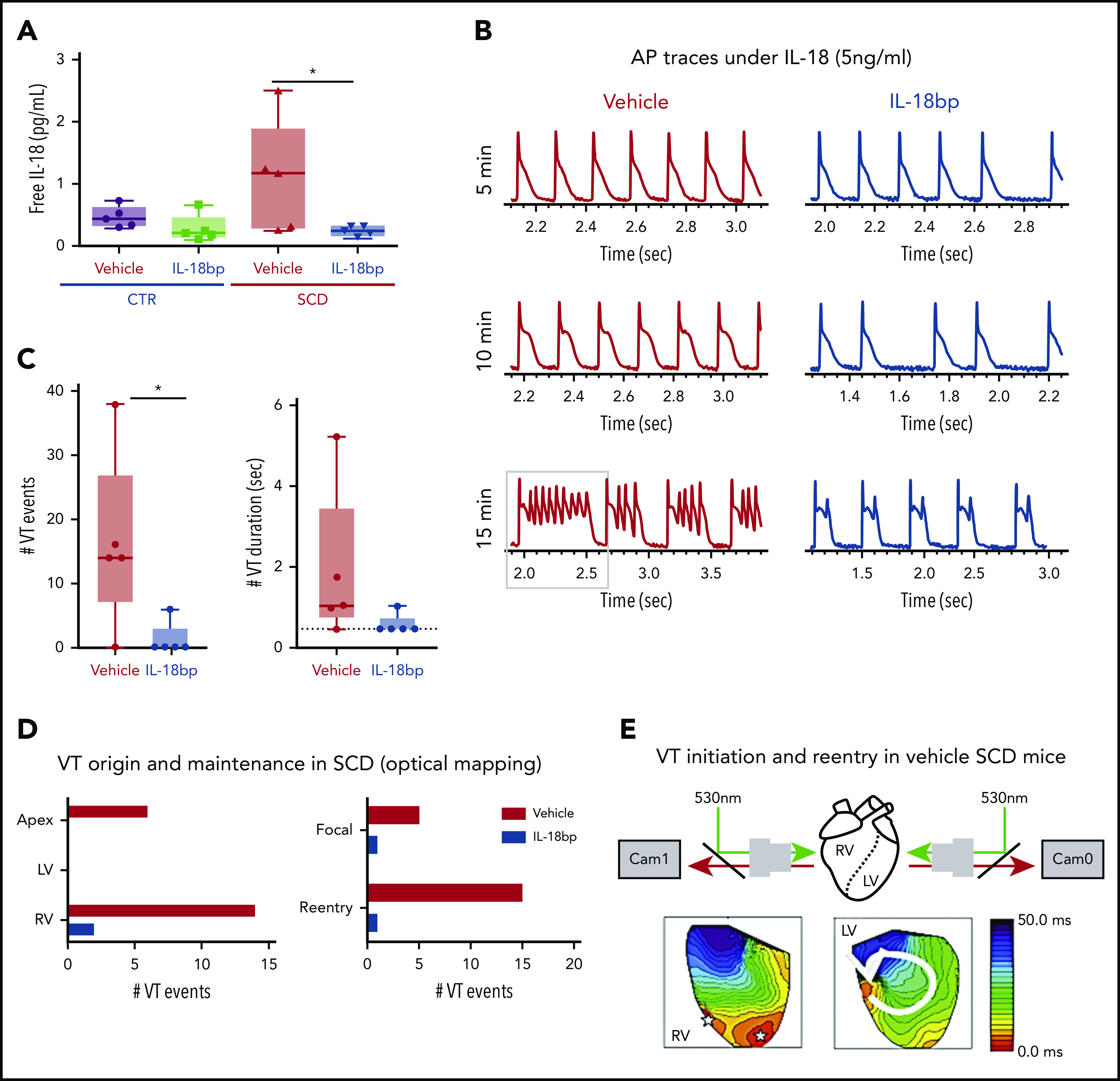
IL-18BP treatment prevents VT initiations under IL-18 exposure in murine SCD hearts. (A) Free IL-18 levels were higher in SCD mice compared with CTR mice, both with exposure to vehicle for 4 weeks, and reduced with IL-18BP exposure for 4 weeks in SCD mice compared with vehicle administration (CTR + vehicle, 0.46 ± 0.07 pg/mL; CTR + IL-18BP, 0.28 ± 0.09 pg/mL; SCD + vehicle, 1.13 ± 0.35 pg/mL; SCD + IL-18BP, 0.24 ± 0.03 pg/mL; ANOVA P = .026; n = 5 for each group). (B) Representative AP and VT traces under IL-18 in vehicle and IL-18BP treated hearts in the presence of 5 ng/mL IL-18. PVCs and VT were frequently induced in vehicle-treated hearts (n = 4 of 5) compared with IL-18BP-treated hearts (n = 1 of 5). (C) IL-18BP treatment suppressed incidence of VT events and VT duration. (D) Focal activity from RV and reentry formations were markedly reduced in the IL-18BP group. (E) Activation maps from the RV and LV showed that focal activity from the RV formed reentry to initiate a transient VT shown in panel B (gray box represents the VT episode that was used for activation maps shown in panel E). Median values displayed with whiskers using the Tukey method. *P < .05. Horizontal bar in panels A and C signify mean of values. Error bars represent standard error. Cam0, camera 0; Cam1, camera 1.
