Figure 1.
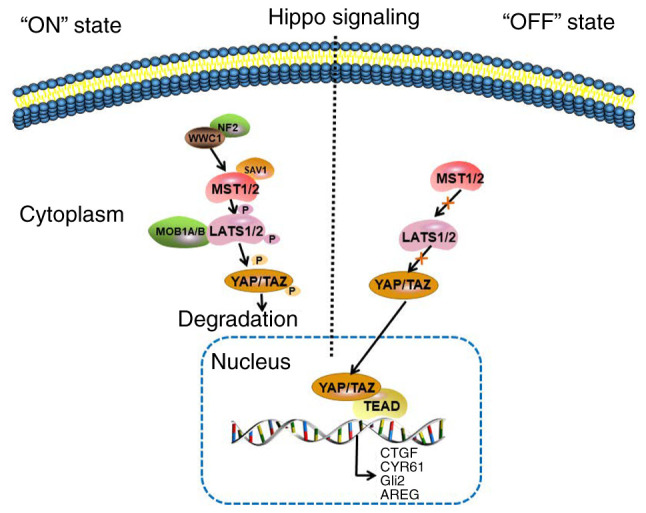
Hippo signaling pathway. In response to high cell density, NF2 and WWC1 activate the Hippo signaling pathway by binding to LATS1/2 to facilitate their activation by MST1/2. In turn, MST1/2 bind to the cofactor, SAV1, to form an enzymatic complex that phosphorylates and activates the LATS1/2 kinases, and the MOB1A/B regulatory subunits of LAST1/2. Subsequently, LATS1/2 phosphorylate the transcriptional coactivators, YAP and TAZ, which in turn translocate in the cytoplasm and get inactivated. In cancer, the Hippo signaling is abnormally inactivated and LATS1/2 are not activated by MST1/2. The YAP/TAZ complex translocates to the nucleus and binds with TEAD to activate the transcription of its target genes, including CTGF, CYR61, Gli2 and AREG. NF2, neurofibromatosis type 2; WWC1, WW And C2 domain containing 1 gene; LATS1/2, large tumor suppressors 1 and 2; MST1/2, upstream sterile 20-like kinase 1 and 2; SAV1, Salvador homologue 1; MOB1A/B, MOB kinase activator 1A and B; YAP, Yes-associated protein; TAZ, transcriptional coactivator with PDZ-binding motif; TEAD, transcriptional enhancer factor domain; CTGF, connective tissue growth factor; CYR61, cysteine-rich angiogenic inducer 61; Gli2, glioma-associated oncogene family zinc finger 2; AREG, amphiregulin.
