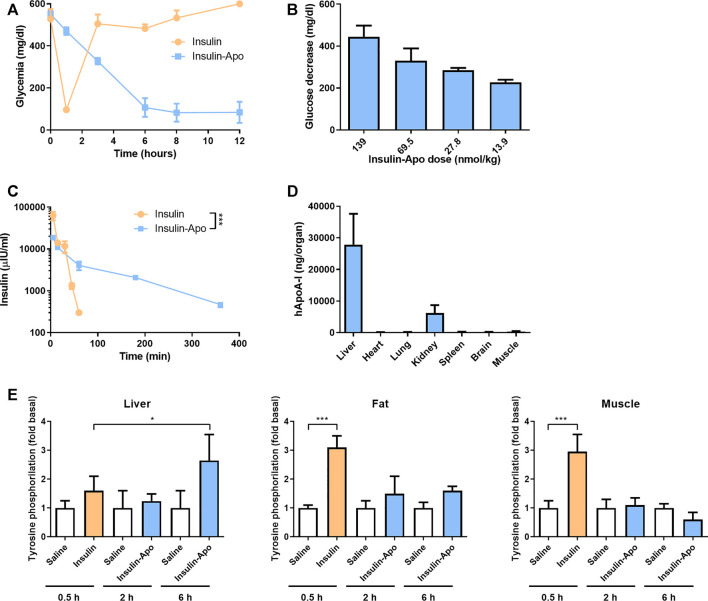
FIGURE 2.
Insulin-Apo pharmacokinetics/pharmacodynamics after intravenous administration. (A) Streptozotocin-induced diabetic C57BL/6J mice received 139 nmol/kg insulin or Insulin-Apo i.v. At various time points, mice were bled, and glycemia was determined with a glucometer (n = 3). (B) Reduction in glycemia 6 h after administration of different doses of Insulin-Apo i.v. to streptozotocin-induced diabetic C57BL/6J mice. (C) C57BL/6J mice received 55 nmol/kg of insulin or, Insulin-Apo i.v. At various time points, mice were bled and samples assayed by ELISA for the presence of human serum insulin (n = 3). ***p < 0.001. (D) To analyze biodistribution, C57BL/6J mice received 110 nmol/kg Insulin-Apo i.v. Three hours after administration, the animals were sacrificed, and several organs were removed. The amount of human apoA-I in the organ homogenates was determined by ELISA (n = 4). (E) Tyrosine phosphorylation of the insulin receptor in liver, fat tissue, and muscle was determined by Western blot of tissue samples from C57BL/6J mice 0.5 h after treatment with 1 U/kg s.c. human insulin and 2 and 6 h after treatment with 200 nmol/kg s.c. Insulin-Apo (n = 3).