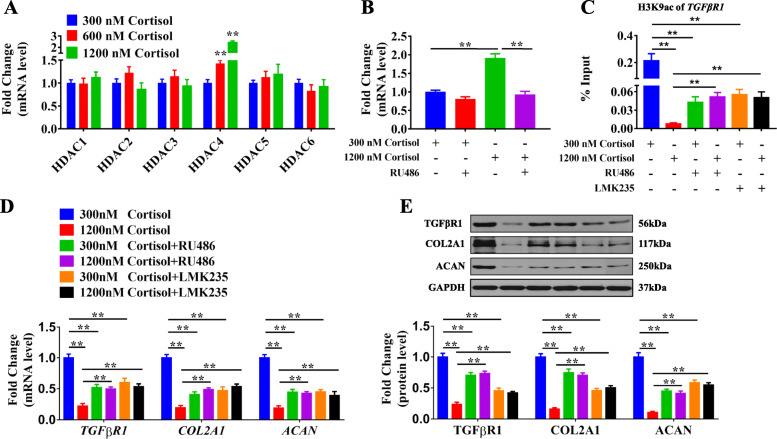
Fig. 4.
GR/HDAC4 mediated the H3K9 deacetylation of TGFβRI induced by high levels of cortisol. a RT-qPCR analysis of HDACs expression in the WJ-MSCs treated with 300, 600, and 1200 nM cortisol after chondrogenic differentiation for 7 days. n = 5. b RT-qPCR analysis of HDAC4 expression in WJ-MSCs treated with cortisol and RU486 (10 μM) after chondrogenic differentiation for 7 days. n = 5. c ChIP-PCR analysis of the H3K9ac level of TGFβRI in WJ-MSCs treated with cortisol, and RU486 (10 μM) or LMK235 (100 nM) after chondrogenic differentiation for 7 days. n = 3. d RT-qPCR analysis of TGFβRI, COL2A1, and ACAN expression in WJ-MSCs treated with cortisol and RU486 (10 μM) or LMK235 (100 nM) after chondrogenic differentiation for 7 days. n = 5. e Western blot analysis of TGFβRI, COL2A1, and ACAN in WJ-MSCs treated with cortisol, RU486 (10 μM), or LMK235 (100 nM) after chondrogenic differentiation for 7 days, n = 5. RT-qPCR, real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction; GR, glucocorticoid receptor; HDAC4, histone deacetylase 4; H3K9ac, histone 3 lysine 9 acetylation; TGFβRI, transforming growth factor β receptor I; WJ-MSCs, Wharton’s jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells; ChIP-PCR, chromatin immunoprecipitation-polymerase chain reaction; igG, immunoglobulin G. Data are the mean ± S.E.M. **P < 0.01 vs control