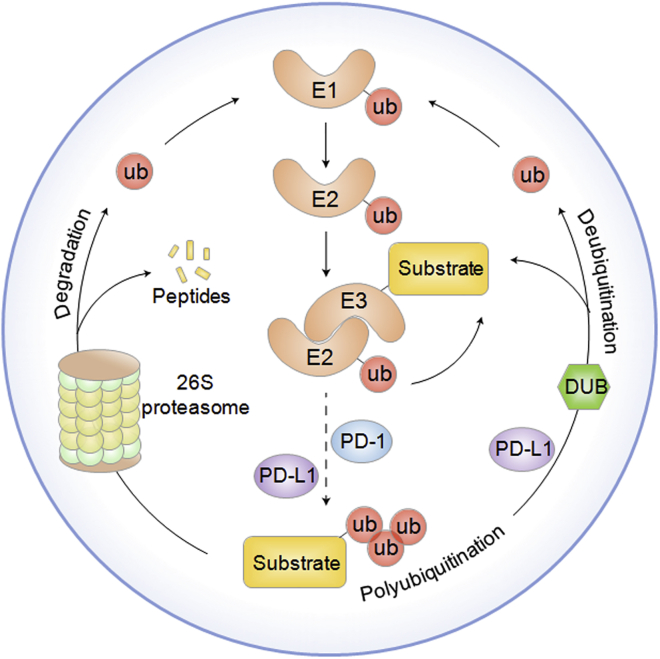
Figure 1.
The Ubiquitination and Deubiquitination Processes Are Illustrated
The ubiquitin-proteasome system is composed of ubiquitin, ubiquitin-activating enzymes (E1s), ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes (E2s), ubiquitin-protein enzymes (E3s), deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs), and the 26S proteasome. Ubiquitination has a series of enzyme-linked reactions mediated by E1, E2, and E3 ligases. The carboxyl group (-COOH) of the C terminus of ubiquitin binds to an E1 cysteine residue along with ATP and is thus stimulated by a thioester link with E1. The E2 ligase temporarily transfers ubiquitin moieties with a thioester linkage. Activated ubiquitin is moved from E2 to the lysine residue on substrates by E3. Ubiquitination is controlled by E3 ligases, whose activities can be reversed by DUBs. Ubiquitination and deubiquitination play a crucial role in the regulation of PD-1/PD-L1 in cancer.