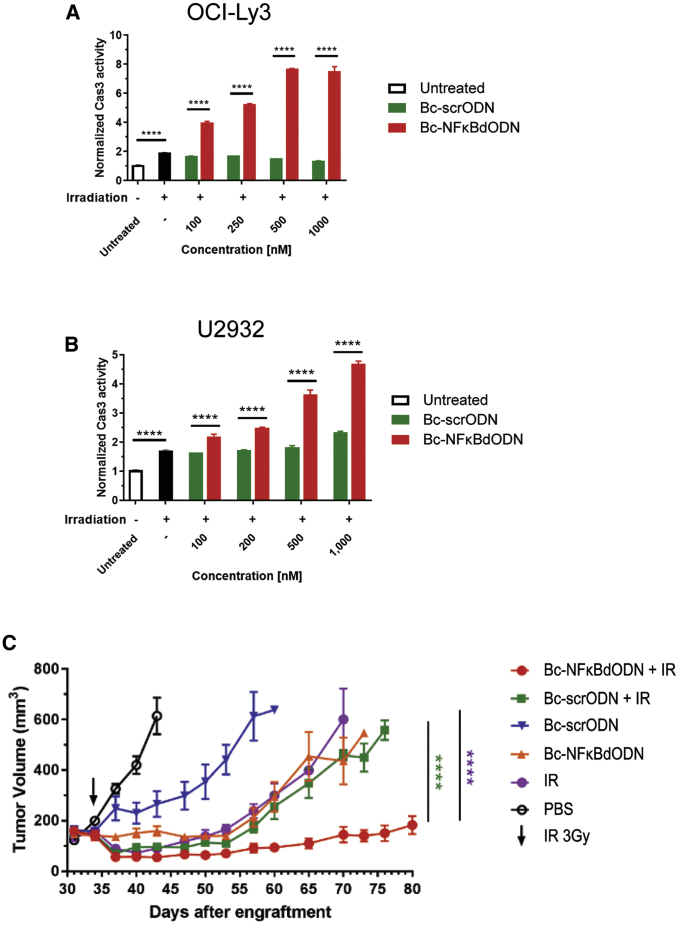
Figure 4.
Targeted NF-κB Inhibition Sensitizes Lymphoma to Radiation Therapy
(A and B) OCI-Ly3 (A) and U2932 (B) cells treated using Bc-NFκBdODN or Bc-scrODN were irradiated using 2.5 or 10 Gy for radiosensitive OCI-Ly3 or radioresistant U2932 cells, respectively, before the assessment of cell death by measuring the caspase-3 activation. Shown are representative results from three independent experiments in triplicates (means ± SD). (C) Local administration of Bc-NFκBdODN augments antitumor efficacy of human lymphoma irradiation. Immunodeficient NSG mice with established subcutaneously engrafted OCI-Ly3 lymphomas were injected intratumorally with 10 mg/kg Bc-NFκBdODN, Bc-scrODN, or PBS alone daily, with a single 3-Gy dose of irradiation 2 days after the initial treatment. Tumor progression was analyzed using caliper measurements. Means ± SEM are shown (n = 5/group).