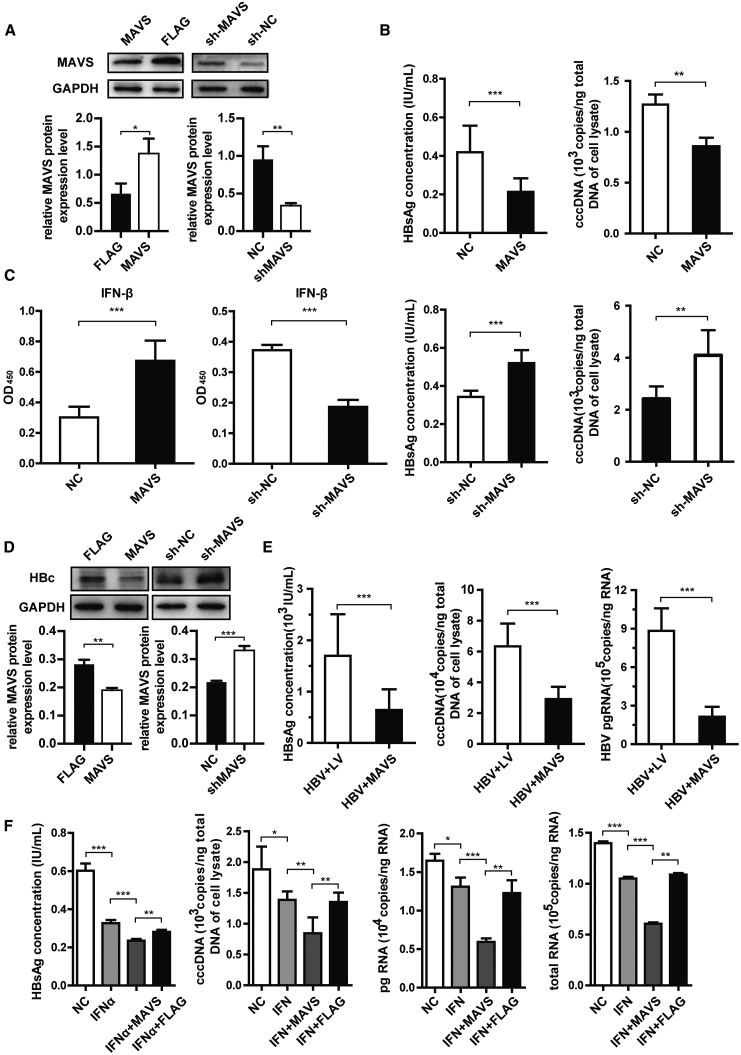
Figure 4.
MAVS Inhibits the Expression Levels of HBV Markers In Vitro
(A) HepG2.2.15 cells were transfected with MAVS-overexpressing or knockdown (sh-MAVS) plasmid. Western blot analysis of MAVS protein expression normalized to GAPDH, which served as a protein loading control and IHC of cell-attached slides assay detected the HBx protein expression level are shown. (B) ELISA analysis of HBsAg in HepG2.2.15 cell supernatants and qRT-PCR determination of HBV cccDNA levels. Cells were transfected with the MAVS overexpression or knockdown plasmid. (C) ELISA analysis of IFN-β expression in HepG2.2.15 cells in MAVS overexpression, NC-FLAG, sh-MAVS, and sh-NC groups. (D) Western blot analysis and quantification of HBc expression in HepG2.2.15 cells in MAVS overexpression, NC-FLAG, sh-MAVS, and sh-NC groups. (E) ELISA analysis of HBsAg in HepG2.2.15 cell supernatants and qRT-PCR determination of HBV DNA, cccDNA, and pgRNA levels. Cells were co-transfected with the HBV and MAVS overexpression or NC plasmid. (F) HepG2.2.15 cells were transfected with MAVS-overexpressing plasmid or the empty FLAG vector and treated with or without IFN-α. ELISA analysis of HBsAg in HepG2.2.15 cell supernatants and qRT-PCR determination of HBV cccDNA and HBV pgRNA levels are shown. Data represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001.