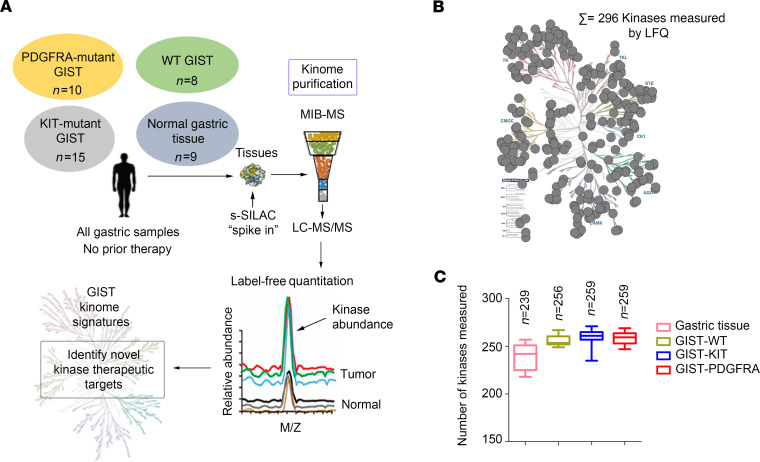
Figure 1. Characterizing the GIST kinome in primary tumors using MIB-MS to identify therapeutic targets.
(A) Schematic of experimental approach. MIB-MS was used to quantify the kinase abundance in patients with GISTs (untreated, gastric primary GIST from 3 molecular subtypes: KIT mutant, n = 15; PDGFRA mutant, n = 10; WT GIST, n = 8; and normal gastric tissue, n = 9) to map the proteomic landscape of the kinome and identify targets. Kinase levels in tissues were determined using a combination of LFQ and s-SILAC. (B) Kinome tree depicts fraction of kinome quantitated by MIB-MS and frequency across 42 samples measured. (C) Average number of kinases detected by MIB-MS profiling broken down by tissue type. GIST, gastrointestinal stromal tumor; MIB-MS, multiplexed inhibitor beads and mass spectrometry; LFQ, label-free quantitation; s-SILAC, super-SILAC.