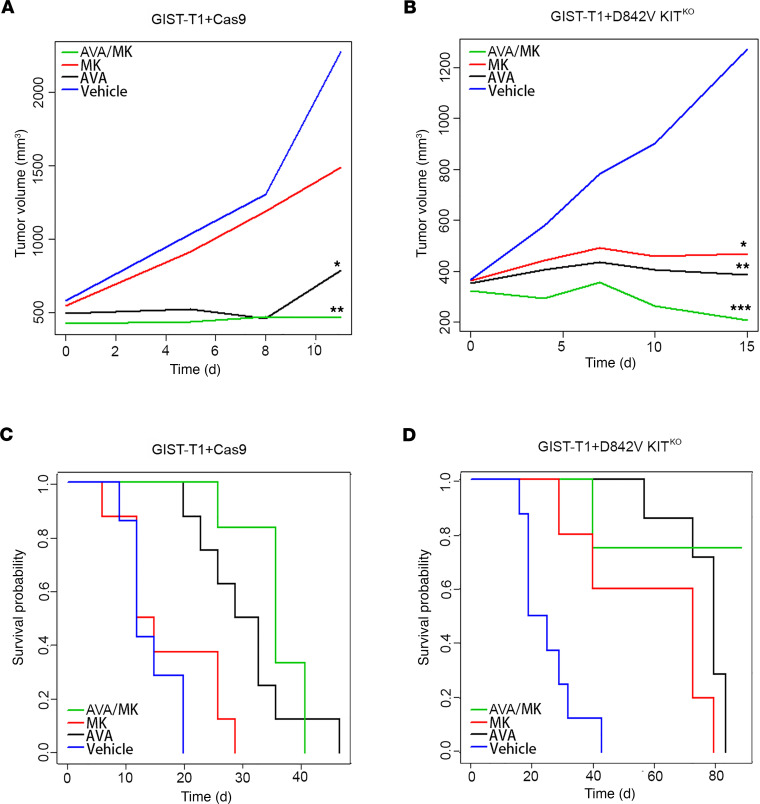
Figure 6. The combination of MK-1775 and avapritinib significantly inhibits GIST growth in vivo and improves disease-specific survival.
(A) Statistically significant decreases in the rate of GIST-T1+Cas9 xenograft tumor growth were observed due to treatment with avapritinib (*P = 0.05, black) and avapritinib+MK-1775 combination (**P = 0.002, green) compared with vehicle group (blue) on day 11. (B) Statistically significant decreases in the rate of GIST-T1+D842V KITKO xenograft tumor growth were observed due to treatment with avapritinib (**P = 0.002) and MK-1775 (*P = 0.02) and avapritinib+MK-1775 (***P ≤ 0.0002) compared with vehicle group on day 15. Smoothed tumor growth curves (tumor volume vs. time) were computed for each treatment using the lowess smoother in the R statistical language. (C) Kaplan-Meier estimate of the probability of disease-specific survival of GIST-T1+Cas9 xenografts. Statistically significant differences (even after adjusting for multiple testing) in disease-specific survival were observed between the following comparisons: vehicle vs. avapritinib (P < 0.0001); vehicle vs. avapritinib/MK-1775 (P < 0.0001); and MK-1775 vs. avapritinib/MK-1775 (P < 0.0001). (D) Kaplan-Meier estimate of the probability of disease-specific survival of GIST-T1+D842V KITKO xenografts. Statistically significant differences (even after adjusting for multiple testing) in disease-specific survival were observed between the following comparisons: vehicle vs. MK-1775 (P = 0.01); vehicle vs. avapritinib (P < 0.0001); vehicle vs. avapritinib/MK-1775 (P < 0.0001); MK-1775 vs. avapritinib/MK-1775 (P = 0.01); and avapritinib vs. avapritinib/MK-1775 (P = 0.02). The overall test is also significant (P < 0.0001). GIST, gastrointestinal stromal tumor.