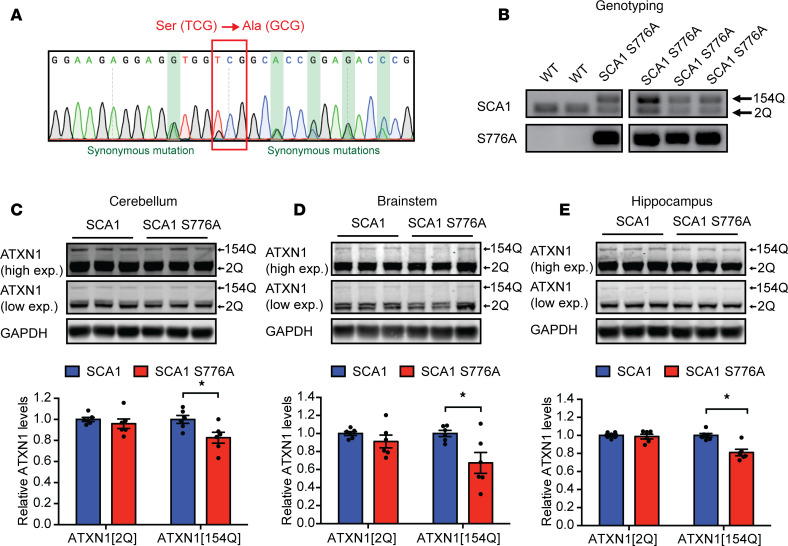
Figure 2. Disruption of S776 phosphorylation reduces polyQ-expanded ATXN1[154Q] levels in the cerebellum, brainstem, and hippocampus.
(A) Sanger sequencing confirming serine-to-alanine mutation at position 776 and synonymous mutations in heterozygous Atxn1154Q[S776A]/2Q F1 offspring upon CRISPR injections. (B) Genotyping of F1 offspring using specific primers to distinguish WT and SCA1 mice as well as primers for the detection of the S776A allele. Representative Western blots and quantifications of ATXN1[2Q] and ATXN1[154Q] protein levels in the (C) cerebellum, (D) brainstem, and (E) hippocampus of 6-week-old Atxn1154Q/2Q (SCA1) and Atxn1154Q[S776A]/2Q (SCA1 S776A) mice. For each assay, a minimum of 6 replicates were performed. Simple comparisons used Student’s t test. *P < 0.05. All data represent means ± SEM.