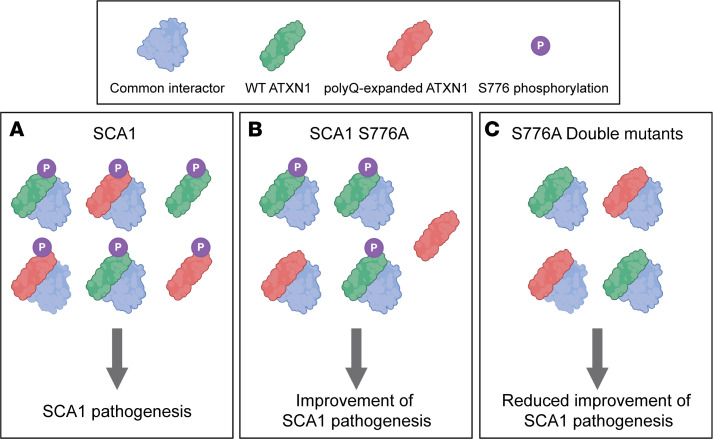
Figure 8. Proposed model for the neuroprotective function of WT ATXN1 in SCA1.
The model illustrates the association of polyQ-expanded ATXN1 and WT ATXN1 into common complexes in Atxn1154Q/2Q (SCA1) and Atxn1154Q[S776A]/2Q (SCA1 S776A) and Atxn1154Q[S776A]/2Q[S776A] (S776A double mutants). (A) SCA1: WT ATXN1 competes with polyQ-expanded ATXN1 for the association with common interactors and forms toxic complexes leading to SCA1 pathogenesis. (B) SCA1 S776A: Disruption of S776 phosphorylation on the polyQ-expanded ATXN1 decreases its levels and reduces the formation of toxic complexes, resulting in an improvement of SCA1 pathogenesis. (C) S776A double mutants: Disruption of S776 phosphorylation on both alleles decreases polyQ-expanded ATXN1 and WT ATXN1. The reduction of WT ATXN1 decreases its association with common interactors, which then interact with polyQ-expanded ATXN1 to form toxic complexes, thereby reducing the rescue effect. The illustration was created using BioRender.com.