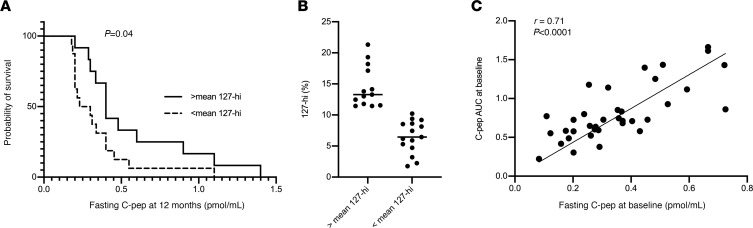
Figure 4. The probability of preserving β cell function is greater in patients with a higher relative frequency of 127-hi cells at diagnosis.
(A) The relative frequency of 127-hi cells was determined in PBMCs collected by ITN (n = 9) and SRDRI (n = 19) at baseline from patients with T1D with good glucose control. Fasting C-peptide levels were measured in each patient at 12 months after diagnosis. Patients were stratified into groups based on having either equal to or greater than the mean frequency of 127-hi cells (n = 13, solid line) or lower than the mean frequency of 127-hi cells (n = 15, dashed line) at baseline. Statistical significance was determined using the log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test. (B) The relative frequency of 127-hi cells at baseline for patient data used in the analysis shown in A. Each symbol represents an individual patient. (C) In a different cohort of patients with good glucose control, fasting C-peptide levels and stimulated C-peptide AUC were measured at baseline and the correlation between the 2 C-peptide values was determined using Spearman’s correlation (n = 36).