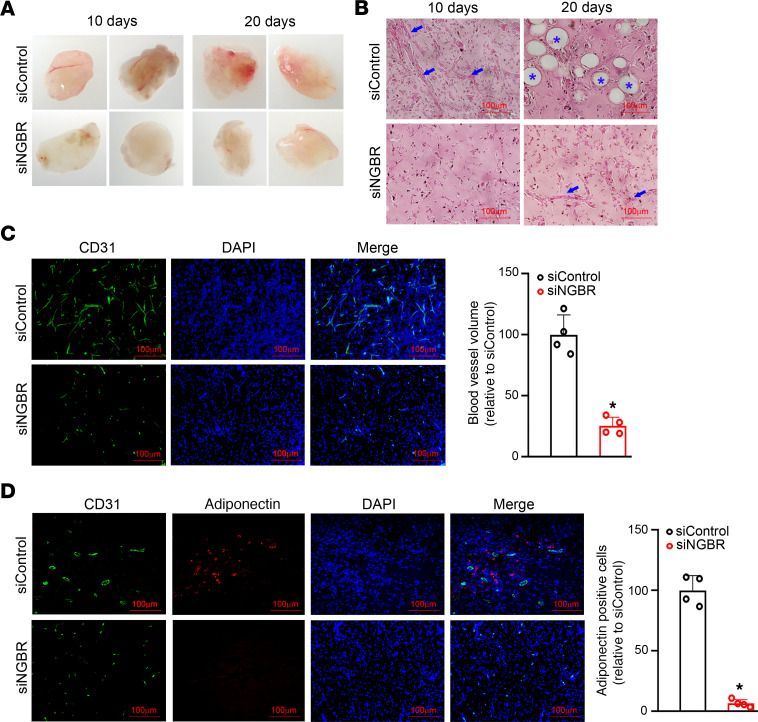
Figure 7. NGBR is required for the differentiation of HemSCs to blood vessels or adipocytes in vivo.
(A) Representative images of implants isolated from the nude mice are shown in the left panel. Clonal siControl or siNGBR HemSCs were suspended in Matrigel and injected into nude mice. The implants were collected at indicated time points (day 10 and day 20). NGBR knockdown reduced the angiogenesis and adipogenesis in the implants of HemSCs. (B) H&E staining of siControl and siNGBR HemSCs implants at the corresponding time points. Clonal HemSCs at passage 5 were used. Arrows point to the blood vessels, and stars point to the adipocytes. (C) IF staining of day 10 implants. IF staining of human CD31 (green) is shown on the left, followed by DAPI (blue) staining and a merged image. NGBR depletion decreased blood vessel formation on day 10. Quantitative analysis of positive CD31 staining was carried out using ImageJ software. *P < 0.05 vs. control (siControl) (n = 4). (D) IF staining of implants on day 20. IF staining of human CD31 (green) is shown on the left, followed by adiponectin (red) and DAPI (blue) staining, and a merged image. NGBR depletion decreased adipogenesis on day 20. Quantitative analysis of positive adiponectin staining was carried out using ImageJ software. *P < 0.05 vs. control (siControl) (n = 4). Scale bar: 100 μm. Statistical analyses: 2-tailed unpaired Student’s t test (C and D); data are expressed as mean ± SEM. NGBR, NOGOB receptor; HemSCs, hemangioma stem cells; siControl, control siRNA; siNGBR, NGBR siRNA.