Fig. 1.
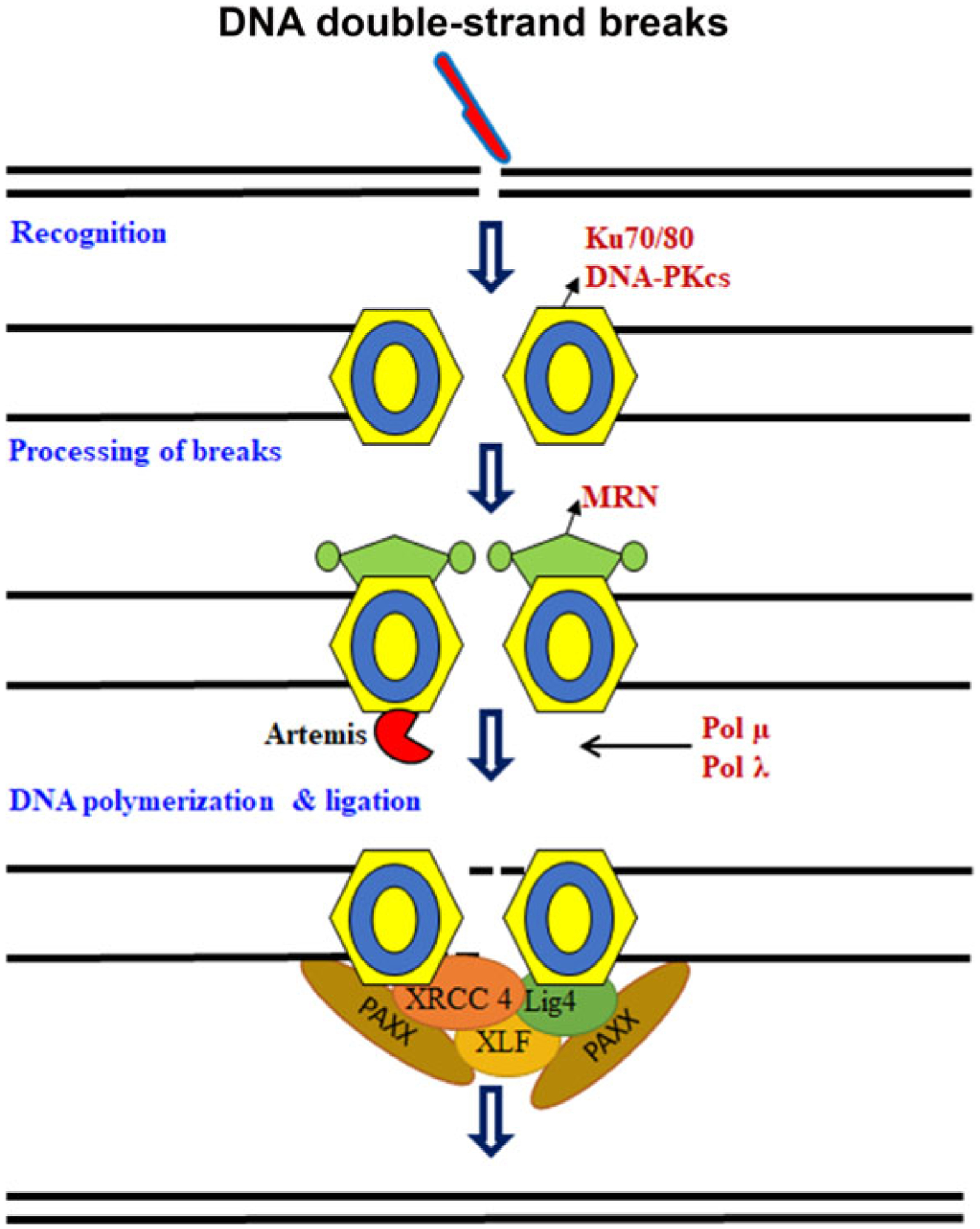
Schematic representation of non-homologous end joining. DNA double-strand break (DSBs) formation is detected by the Ku70/80–DNA-PKcs (DNA-dependent protein kinase). The ends are processed by MRN complex (MRE11, meiotic recombination11; NBS1, Nijmegen breakage syndrome 1). The gaps are filled by polymerase μ and λ and ligated by DNA ligase IV (LIG4). Artemis, X-ray cross-complementing protein 4 (XRCC4), and XRCC4-like factor (XLF; also called Cernunnos) playing a prime role in recruiting LIG4 to carry out the DSBs-joining reaction.
