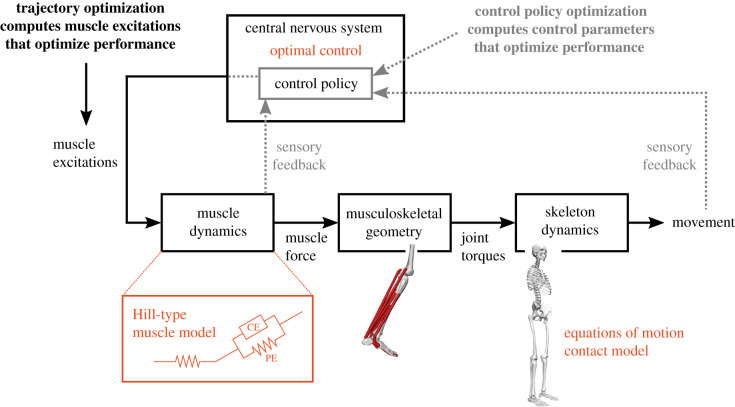
Figure 2.
Schematic of predictive simulation approaches using trajectory optimization and control policy optimization. Both approaches are based on a model of the musculoskeletal system. Muscle dynamics describe how muscles transform excitations into forces. Commonly, Hill-type muscle models are used (PE, passive element; CE, contractile element). Musculoskeletal geometry determines how these forces are applied to the skeleton system. Skeleton dynamics describe how the skeleton moves under the influence of joint torques and contact forces with the environment. It is commonly assumed that motor control is optimal in some sense, for example, by minimizing muscle effort, within the constraints imposed by the musculoskeletal system. Trajectory optimization computes open-loop muscle excitations, whereas in control policy optimization the control policy is modelled and control parameters are computed. (Online version in colour.)